Inhibitors of HCV NS5A: From Iminothiazolidinones to Symmetrical Stilbenes
- PMID: 24900306
- PMCID: PMC4017990
- DOI: 10.1021/ml1002647
Inhibitors of HCV NS5A: From Iminothiazolidinones to Symmetrical Stilbenes
Abstract
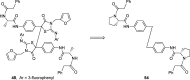
The iminothiazolidinone BMS-858 (2) was identified as a specific inhibitor of HCV replication in a genotype 1b replicon assay via a high-throughput screening campaign. A more potent analogue, BMS-824 (18), was used in resistance mapping studies, which revealed that inhibitory activity was related to disrupting the function of the HCV nonstructural protein 5A. Despite the development of coherent and interpretable SAR, it was subsequently discovered that in DMSO 18 underwent an oxidation and structural rearrangement to afford the thiohydantoin 47, a compound with reduced HCV inhibitory activity. However, HPLC bioassay fractionation studies performed after incubation of 18 in assay media led to the identification of fractions containing a dimeric species 48 that exhibited potent antiviral activity. Excision of the key elements hypothesized to be responsible for antiviral activity based on SAR observations reduced 48 to a simplified, symmetrical, pharmacophore realized most effectively with the stilbene 55, a compound that demonstrated potent inhibition of HCV in a genotype 1b replicon with an EC50 = 86 pM.
Keywords: HCV NS5A inhibitor; iminothiazolidinone; stilbene.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discovery of potent hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitors with dimeric structures.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Aug;55(8):3795-802. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00146-11. Epub 2011 May 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21576451 Free PMC article.
-
HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitors. Part 2: investigation of stilbene prolinamides.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Oct 1;22(19):6063-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.08.049. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22959243
-
HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitors. Part 4. Optimization for genotype 1a replicon inhibitory activity.J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 13;57(5):1976-94. doi: 10.1021/jm301796k. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23573957
-
Antiviral activity and resistance of HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitors.Curr Opin Virol. 2013 Oct;3(5):514-20. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23896281 Review.
-
NS5A--from obscurity to new target for HCV therapy.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2008 Jun;3(2):77-92. doi: 10.2174/157489108784746597. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2008. PMID: 18673121 Review.
Cited by
-
The crystal structure of NS5A domain 1 from genotype 1a reveals new clues to the mechanism of action for dimeric HCV inhibitors.Protein Sci. 2014 Jun;23(6):723-34. doi: 10.1002/pro.2456. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24639329 Free PMC article.
-
The Compound SBI-0090799 Inhibits Zika Virus Infection by Blocking De Novo Formation of the Membranous Replication Compartment.J Virol. 2021 Oct 27;95(22):e0099621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00996-21. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34468177 Free PMC article.
-
TARGETING THE NS5A PROTEIN OF HCV: AN EMERGING OPTION.Drugs Future. 2011 Sep;36(9):691-711. doi: 10.1358/dof.2011.036.09.1641618. Drugs Future. 2011. PMID: 23378700 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of potent hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitors with dimeric structures.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Aug;55(8):3795-802. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00146-11. Epub 2011 May 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21576451 Free PMC article.
-
Progress, evolving therapeutic/diagnostic approaches, and challenges in the management of hepatitis C virus infections.Arch Virol. 2022 Mar;167(3):717-736. doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05375-0. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Arch Virol. 2022. PMID: 35089390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim W. R. Global Epidemiology and Burden of Hepatitis C. Microbes Infection 2002, 4, 1219–1225. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle J. H.; Seeff L. B. Peginterferon and Ribavirin for Chronic Hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2444–2451. - PubMed
-
- De Francesco R.; Migliaccio G. Challenges and Successes in Developing New Therapies for Hepatitis C. Nature 2005, 436, 953–960. - PubMed
-
- Gao M.; Nettles R. E.; Belema M.; Snyder L. B.; Nguyen V. N.; Fridell R. A.; Serrano-Wu M. H.; Langley D. R.; Sun J.-H.; O’Boyle D. R.; Lemm J. A.; Wang C.; Knipe J. O.; Chien C.; Colonno R. J.; Grasela D. M.; Meanwell N. A.; Hamann L. G. Chemical Genetics Strategy Identifies an HCV NS5A Inhibitor with a Potent Clinical Effect. Nature 2010, 465, 96–100. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

