Homology Model Versus X-ray Structure in Receptor-based Drug Design: A Retrospective Analysis with the Dopamine D3 Receptor
- PMID: 24900310
- PMCID: PMC4018084
- DOI: 10.1021/ml100288q
Homology Model Versus X-ray Structure in Receptor-based Drug Design: A Retrospective Analysis with the Dopamine D3 Receptor
Abstract
Structure-based design methods commonly used in medicinal chemistry rely on a three-dimensional representation of the receptor. However, few crystal structures are solved in comparison with the huge number of pharmaceutical targets. This often renders homology models the only information available. It is particularly true for G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), one of the most important targets for approved medicines and current drug discovery projects. However, very few studies have tested their validity in comparison with corresponding crystal structures, especially in a lead optimization perspective. The recent solving of dopamine D3 receptor crystal structure allowed us to assess our historical homology model. We performed a statistical analysis, by docking our in-house lead optimization library of 1500 molecules. We demonstrate here that the refined homology model suits at least as well as the X-ray structure. It is concluded that when the crystal structure of a given GPCR is not available, homology modeling can be an excellent surrogate to support drug discovery efforts.
Keywords: Dopamine D3 receptor; G protein-coupled receptors; docking; homology model; lead optimization.
Figures


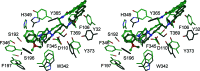
References
-
- Senderowitz H.; Marantz Y. G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Target-based in silico screening. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 4049–4068. - PubMed
-
- de Graaf C.; Rognan D. Customizing G Protein-coupled receptor models for structure-based virtual screening. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 4026–4048. - PubMed
-
- Levoin N.; Calmels T.; Poupardin-Olivier O.; Labeeuw O.; Danvy D.; Robert P.; Berrebi-Bertrand I.; Ganellin C. R.; Schunack W.; Stark H.; Capet M. Refined Docking as a Valuable Tool for Lead Optimization: Application to Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonists. Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 2008, 341, 610–623. - PubMed
-
- Lundstrom K. Latest development in drug discovery on G protein-coupled receptors. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2006, 7, 465–470. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K.; Kumasaka T.; Hori T.; Behnke C. A.; Motoshima H.; Fox B. A.; Trong I. L.; Teller D. C.; Okada T.; Stenkamp R. E.; Yamamoto M.; Miyano M. Crystal Structure of Rhodopsin: A G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 2000, 289, 739–745. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

