SAR Development of Lysine-Based Irreversible Inhibitors of Transglutaminase 2 for Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 24900424
- PMCID: PMC4025666
- DOI: 10.1021/ml300241m
SAR Development of Lysine-Based Irreversible Inhibitors of Transglutaminase 2 for Huntington's Disease
Abstract
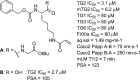
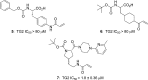
We report a series of irreversible transglutaminase 2 inhibitors starting from a known lysine dipeptide bearing an acrylamide warhead. We established new SARs resulting in compounds demonstrating improved potency and better physical and calculated properties. Transglutaminase selectivity profiling and in vitro ADME properties of selected compounds are also reported.
Keywords: acrylamides; celiac disease; in vitro ADME; plasma stability; polar surface area.
Figures
References
-
- Greenberg C. S.; Birckbichler R. H. Transglutaminases: Multifunctional cross-linking enzymes that stabilize tissues. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 3071–3077. - PubMed
-
- Im M.-J.; Riek P.; Graham R. A novel guanine nucleotide-binding protein coupled to the α1-adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 18952–18960. - PubMed
-
- Lai T.-S.; Slaughter T.; Peoples K.; Hettasch J.; Greenburg C. Regulation of human tissue transglutaminase function by magnesium-nucleotide complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1776–1781. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous