Creation of readily accessible and orally active analogue of cortistatin a
- PMID: 24900528
- PMCID: PMC4025756
- DOI: 10.1021/ml300143d
Creation of readily accessible and orally active analogue of cortistatin a
Abstract
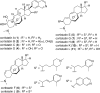
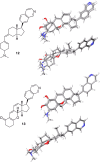
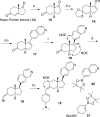
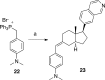
Syntheses of structurally simplified analogues of cortistatin A (1), a novel antiangiogenic steroidal alkaloid from Indonesian marine sponge, and their biological activities were investigated. The analogues were designed by considering the 3-D structure of 1. Compound 30, in which the isoquinoline moiety was appended to the planar tetracyclic core structure, showed potent antiproliferative activity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) together with high selectivity and also showed in vivo antiangiogenic activity and significant antitumor effect by oral administration.
Keywords: Cortistatin A; analogue synthesis; antiangiogenesis; marine sponge; structure−activity relationship.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Creation of readily accessible analogue of cortistatin A as an antitumor drug lead].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(8):867-72. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00159. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 23903226 Review. Japanese.
-
Synthetic studies of cortistatin A analogue from the CD-ring fragment of vitamin D₂.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013;61(10):1024-9. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c13-00375. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013. PMID: 24088693
-
Stereoselective synthesis of core structure of cortistatin A.Org Lett. 2011 Jul 1;13(13):3514-7. doi: 10.1021/ol201327u. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Org Lett. 2011. PMID: 21651309
-
Structure-activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids.Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Nov 1;15(21):6758-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.08.017. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17765550
-
Cephalostatin analogues--synthesis and biological activity.Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 2004;87:1-80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0581-8_1. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 2004. PMID: 15079895 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Mycobacterial N-(2-Arylethyl)quinolin-3-amines Inspired by Marine Sponge-Derived Alkaloid.Molecules. 2022 Dec 8;27(24):8701. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248701. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557834 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Antitumor and Anti-Angiogenesis Activity of Pyrone- or Pyridone-Embedded Analogs of Cortistatin A.Mar Drugs. 2025 Apr 20;23(4):179. doi: 10.3390/md23040179. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40278300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet P.; Jain R. K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. - PubMed
-
- Aoki S.; Watanabe Y.; Sanagawa M.; Setiawan A.; Kotoku N.; Kobayashi M. Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, Anti-angiogenic Steroidal Alkaloids, from the Marine Sponge Corticium simplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3148–3149. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe Y.; Aoki S.; Tanabe D.; Setiawan A.; Kobayashi M. Cortistatins E, F, G, and H, four novel steroidal alkaloids from marine sponge Corticium simplex. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 4074–4079.
-
- Aoki S.; Watanabe Y.; Tanabe D.; Setiawan A.; Arai M.; Kobayashi M. Cortistatins J, K, L, novel abeo-9(10–19)-androstane-type steroidal alkaloids with isoquinoline unit, from marine sponge Corticium simplex. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 4485–4488.
-
- Aoki S.; Watanabe Y.; Tanabe D.; Arai M.; Suna H.; Miyamoto K.; Tsujibo H.; Tsujikawa K.; Yamamoto H.; Kobayashi M. Structure–activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6758–6762. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

