Discovery, Design, and Optimization of Isoxazole Azepine BET Inhibitors
- PMID: 24900758
- PMCID: PMC4027525
- DOI: 10.1021/ml4001485
Discovery, Design, and Optimization of Isoxazole Azepine BET Inhibitors
Abstract
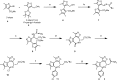
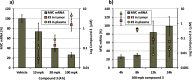
The identification of a novel series of small molecule BET inhibitors is described. Using crystallographic binding modes of an amino-isoxazole fragment and known BET inhibitors, a structure-based drug design effort lead to a novel isoxazole azepine scaffold. This scaffold showed good potency in biochemical and cellular assays and oral activity in an in vivo model of BET inhibition.
Keywords: BET inhibitors; MYC; bromodomain; fragments; isoxazoles.
Figures

References
-
- Wu S. Y.; Chiang C. M. The Double Bromodomain-Containing Chromatin Adaptor Brd4 and Transcriptional Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13141–13145. - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi M.; Ooike S.; Iwata K.; Hikawa H.; Sugahara K.. Antitumor Compounds, WO 2009/084693A1, 9 Sept 2009.
-
- Filippakopoulos P.; Qi J.; Picaud S.; Shen Y.; Smith W. B.; Fedorov O.; Morse E. M.; Keates T.; Hickman T. T.; Felletar I.; Philpott M.; Munro S.; McKeown M. R.; Wang Y.; Christie A. L.; West N.; Cameron M. J.; Schwartz B.; Heightman T. D.; La Thangue N.; French C. A.; Wiest O.; Kung A. L.; Knapp S.; Bradner J. E. Selective Inhibition of BET Bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nicodeme E.; Jeffrey K. L.; Schaefer U.; Beinke S.; Dewell S.; Chung C. W.; Chandwani R.; Marazzi I.; Wilson P.; Coste H.; White J.; Kirilovsky J.; Rice C. M.; Lora J. M.; Prinjha R. K.; Lee K.; Tarakhovsky A. Suppression of Inflammation by a Synthetic Histone Mimic. Nature 2010, 468, 1119–1123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vita M.; Henricksson M.; Myc M. M. Oncoprotein As a Therapeutic Target for Human Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 318–330. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

