Reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome secondary to sunitinib
- PMID: 24900933
- PMCID: PMC4037124
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/952624
Reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome secondary to sunitinib
Abstract
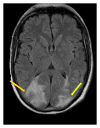
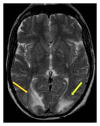
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) is clinical radiologic condition associated with neurological symptoms and cerebral white matter edema. It has been associated with uncontrolled hypertension, eclampsia, immunosuppressants, and more recently the use of antiangiogenic drugs. Sunitinib is an inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor widely used in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). We report a rare case of RPLS occurring on therapy with sunitinib in a patient with RCC. Our aim is to highlight the importance of considering RPLS as a diagnostic possibility and to hold sunitinib for RCC patients presenting with neurologic symptoms.
Figures
References
-
- Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;334(8):494–500. - PubMed
-
- Kou R, Greif D, Michel T. Dephosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by vascular endothelial growth factor. Implications for the vascular responses to cyclosporin A. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277(33):29669–29673. - PubMed
-
- Raps EC, Galetta SL, Broderick M, Atlas SW. Delayed peripartum vasculopathy: cerebral eclampsia revisited. Annals of Neurology. 1993;33(2):222–225. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz RB, Jones KM, Kalina P, et al. Hypertensive encephalopathy: findings on CT, MR imaging, and SPECT imaging in 14 cases. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1992;159(2):379–383. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources