Src kinases regulate de novo actin polymerization during exocytosis in neuroendocrine chromaffin cells
- PMID: 24901433
- PMCID: PMC4047038
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099001
Src kinases regulate de novo actin polymerization during exocytosis in neuroendocrine chromaffin cells
Abstract
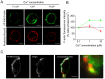
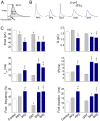
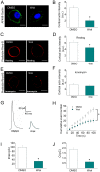
The cortical actin network is dynamically rearranged during secretory processes. Nevertheless, it is unclear how de novo actin polymerization and the disruption of the preexisting actin network control transmitter release. Here we show that in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells, both formation of new actin filaments and disruption of the preexisting cortical actin network are induced by Ca2+ concentrations that trigger exocytosis. These two processes appear to regulate different stages of exocytosis; whereas the inhibition of actin polymerization with the N-WASP inhibitor wiskostatin restricts fusion pore expansion, thus limiting the release of transmitters, the disruption of the cortical actin network with cytochalasin D increases the amount of transmitter released per event. Further, the Src kinase inhibitor PP2, and cSrc SH2 and SH3 domains also suppress Ca2+-dependent actin polymerization, and slow down fusion pore expansion without disturbing the cortical F-actin organization. Finally, the isolated SH3 domain of c-Src prevents both the disruption of the actin network and the increase in the quantal release induced by cytochalasin D. These findings support a model where a rise in the cytosolic Ca2+ triggers actin polymerization through a mechanism that involves Src kinases. The newly formed actin filaments would speed up the expansion of the initial fusion pore, whereas the preexisting actin network might control a different step of the exocytosis process.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Trifaró JM, Rosé SD, Marcu MG (2000) Scinderin, a Ca2+-dependent actin filament severing protein that controls cortical actin network dynamics during secretion. Neurochem Res 25: 133–144. - PubMed
-
- Malacombe M, Bader MF, Gasman S (2006) Exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells: new tasks for actin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763: 1175–1183. - PubMed
-
- Giner D, Neco P, Francés Mdel M, López I, Viniegra S, et al. (2005) Real-time dynamics of the F-actin cytoskeleton during secretion from chromaffin cells. J Cell Sci 118: 2871–2880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

