Structure-function relationship of SW-AT-1, a serpin-type protease inhibitor in silkworm
- PMID: 24901510
- PMCID: PMC4047069
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099013
Structure-function relationship of SW-AT-1, a serpin-type protease inhibitor in silkworm
Abstract
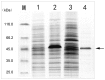
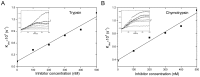
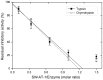
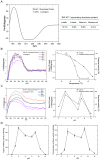
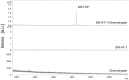
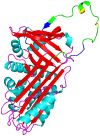
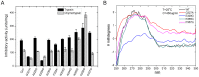
Although SW-AT-1, a serpin-type trypsin inhibitor from silkworm (Bombyx mori), was identified in previous study, its structure-function relationship has not been studied. In this study, SW-AT-1 was cloned from the body wall of silkworm and expressed in E. coli. rSW-AT-1 inhibited both trypsin and chymotrypsin in a concentration-dependent manner. The association rate constant for rSW-AT-1 and trypsin is 1.31×10-5 M-1s-1, for rSW-AT-1 and chymotrpsin is 2.85×10-6 M-1s-1. Circular dichroism (CD) assay showed 33% α-helices, 16% β-sheets, 17% turns, and 31% random coils in the secondary structure of the protein. Enzymatic and CD analysis indicated that rSW-AT-1 was stable at wide pH range between 4-10, and exhibited the highest activity at weakly acidic or alkaline condition. The predicted three-dimensional structure of SW-AT-1 by PyMOL (v1.4) revealed a deductive reactive centre loop (RCL) near the C-terminus, which was extended from the body of the molecule. In addition to trypsin cleavage site in RCL, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry indicated that the chymotrypsin cleavage site of SW-AT-1 was between F336 and T337 in RCL. Directed mutagenesis indicated that both the N- and C-terminal sides of RCL have effects on the activity, and G327 and E329 played an important role in the proper folding of RCL. The physiological role of SW-AT-1 in the defense responses of silkworm were also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Carrell RW, Pemberton PA, Boswell DR (1987) The Serpins: Evolution and adaptation in a family of protease Inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 52: 527–535. - PubMed
-
- Grigoryev SA, Woodcock CL (1998) Chromatin structure in granulocytes. A link between tight compaction and accumulation of a heterochromatin-associated protein (MENT). J Biol Chem 273: 3082–3089. - PubMed
-
- Irving JA, Shushanov SS, Pike RN, Popova EY, Bromme D, et al. (2002) Inhibitory activity of a heterochromatin-associated serpin (MENT) against papain-like cysteine proteinases affects chromatin structure and blocks cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 277: 13192–13201. - PubMed
-
- Ligoxygakis P, Roth S, Reichhart JM (2003) A serpin regulates dorsalventral axis formation in the Drosophila embryo. Curr Biol 13: 2097–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

