Ancient DNA analysis of 8000 B.C. near eastern farmers supports an early neolithic pioneer maritime colonization of Mainland Europe through Cyprus and the Aegean Islands
- PMID: 24901650
- PMCID: PMC4046922
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004401
Ancient DNA analysis of 8000 B.C. near eastern farmers supports an early neolithic pioneer maritime colonization of Mainland Europe through Cyprus and the Aegean Islands
Abstract
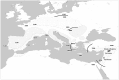
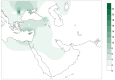
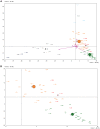
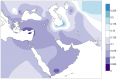
The genetic impact associated to the Neolithic spread in Europe has been widely debated over the last 20 years. Within this context, ancient DNA studies have provided a more reliable picture by directly analyzing the protagonist populations at different regions in Europe. However, the lack of available data from the original Near Eastern farmers has limited the achieved conclusions, preventing the formulation of continental models of Neolithic expansion. Here we address this issue by presenting mitochondrial DNA data of the original Near-Eastern Neolithic communities with the aim of providing the adequate background for the interpretation of Neolithic genetic data from European samples. Sixty-three skeletons from the Pre Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) sites of Tell Halula, Tell Ramad and Dja'de El Mughara dating between 8,700-6,600 cal. B.C. were analyzed, and 15 validated mitochondrial DNA profiles were recovered. In order to estimate the demographic contribution of the first farmers to both Central European and Western Mediterranean Neolithic cultures, haplotype and haplogroup diversities in the PPNB sample were compared using phylogeographic and population genetic analyses to available ancient DNA data from human remains belonging to the Linearbandkeramik-Alföldi Vonaldiszes Kerámia and Cardial/Epicardial cultures. We also searched for possible signatures of the original Neolithic expansion over the modern Near Eastern and South European genetic pools, and tried to infer possible routes of expansion by comparing the obtained results to a database of 60 modern populations from both regions. Comparisons performed among the 3 ancient datasets allowed us to identify K and N-derived mitochondrial DNA haplogroups as potential markers of the Neolithic expansion, whose genetic signature would have reached both the Iberian coasts and the Central European plain. Moreover, the observed genetic affinities between the PPNB samples and the modern populations of Cyprus and Crete seem to suggest that the Neolithic was first introduced into Europe through pioneer seafaring colonization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Childe VG (1957) The Dawn of European Civilization. 6th Revised edition. New York: Alfred A. Knopf Inc. 366 p.
-
- Ammerman A, Cavalli-Sforza LL (1984) The Neolithic Transition and the Genetics of Populations in Europe. Princeton Univ Pr. 200 p.
-
- Price TD (2000) Europe's First Farmers. Cambridge University Press. 395 p.
-
- Renfrew C (1987) Archaeology and language: the puzzle of Indo-European origins. CUP Archive. 372 p.
-
- Piggott S (1965) Ancient Europe. Edinburgh, United Kingdom: Edinburgh University Press. 420 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

