Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials
- PMID: 24904092
- PMCID: PMC4279733
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013101138
Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials
Abstract
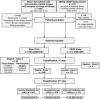
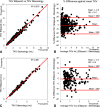
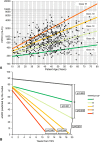
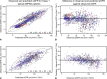
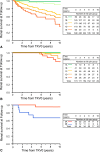
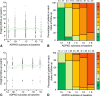
The rate of renal disease progression varies widely among patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), necessitating optimal patient selection for enrollment into clinical trials. Patients from the Mayo Clinic Translational PKD Center with ADPKD (n=590) with computed tomography/magnetic resonance images and three or more eGFR measurements over ≥6 months were classified radiologically as typical (n=538) or atypical (n=52). Total kidney volume (TKV) was measured using stereology (TKVs) and ellipsoid equation (TKVe). Typical patients were randomly partitioned into development and internal validation sets and subclassified according to height-adjusted TKV (HtTKV) ranges for age (1A-1E, in increasing order). Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Study of PKD (CRISP) participants (n=173) were used for external validation. TKVe correlated strongly with TKVs, without systematic underestimation or overestimation. A longitudinal mixed regression model to predict eGFR decline showed that log2HtTKV and age significantly interacted with time in typical patients, but not in atypical patients. When 1A-1E classifications were used instead of log2HtTKV, eGFR slopes were significantly different among subclasses and, except for 1A, different from those in healthy kidney donors. The equation derived from the development set predicted eGFR in both validation sets. The frequency of ESRD at 10 years increased from subclass 1A (2.4%) to 1E (66.9%) in the Mayo cohort and from 1C (2.2%) to 1E (22.3%) in the younger CRISP cohort. Class and subclass designations were stable. An easily applied classification of ADPKD based on HtTKV and age should optimize patient selection for enrollment into clinical trials and for treatment when one becomes available.
Keywords: ADPKD; cystic kidney; kidney volume; polycystic kidney disease; progression of chronic renal failure; survival.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 369: 1287–1301, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Grantham JJ: Clinical practice. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 359: 1477–1485, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Grantham JJ, Torres VE, Chapman AB, Guay-Woodford LM, Bae KT, King BF, Jr, Wetzel LH, Baumgarten DA, Kenney PJ, Harris PC, Klahr S, Bennett WM, Hirschman GN, Meyers CM, Zhang X, Zhu F, Miller JP, CRISP Investigators : Volume progression in polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 354: 2122–2130, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Bost JE, Torres VE, Guay-Woodford L, Bae KT, Landsittel D, Li J, King BF, Martin D, Wetzel LH, Lockhart ME, Harris PC, Moxey-Mims M, Flessner M, Bennett WM, Grantham JJ: Kidney volume and functional outcomes in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 479–486, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Torres VE, Perrone RD, Steinman TI, Bae KT, Miller JP, Miskulin DC, Rahbari Oskoui F, Masoumi A, Hogan MC, Winklhofer FT, Braun W, Thompson PA, Meyers CM, Kelleher C, Schrier RW: The HALT polycystic kidney disease trials: Design and implementation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5: 102–109, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RR00585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000165/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR23940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056956/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000165/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK058816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056961/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR023940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK090728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001417/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK056943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

