Selective modulation of cellular voltage-dependent calcium channels by hyperbaric pressure-a suggested HPNS partial mechanism
- PMID: 24904281
- PMCID: PMC4034351
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00136
Selective modulation of cellular voltage-dependent calcium channels by hyperbaric pressure-a suggested HPNS partial mechanism
Abstract
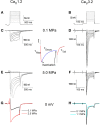
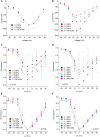
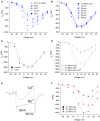
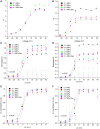
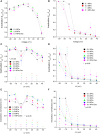
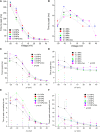
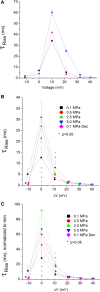
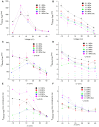
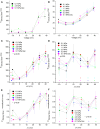
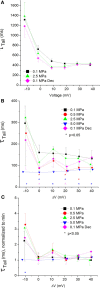
Professional deep sea divers experience motor and cognitive impairment, known as High Pressure Neurological Syndrome (HPNS), when exposed to pressures of 100 msw (1.1 MPa) and above, considered to be the result of synaptic transmission alteration. Previous studies have indicated modulation of presynaptic Ca(2+) currents at high pressure. We directly measured for the first time pressure effects on the currents of voltage dependent Ca(2+) channels (VDCCs) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pressure selectivity augmented the current in CaV1.2 and depressed it in CaV3.2 channels. Pressure application also affected the channels' kinetics, such as ƮRise, ƮDecay. Pressure modulation of VDCCs seems to play an important role in generation of HPNS signs and symptoms.
Keywords: conformational change; high pressure; high pressure neurological syndrome; hyperbaric helium pressure; synaptic transmission; voltage dependency; voltage dependent calcium channels.
Figures
References
-
- Aviner B., Gnatek Y., Gradwohl G., Grossman Y. (2010). Hyperbaric pressure effects on voltage-dependent Ca+2 channels: relevance to HPNS. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 37, 245–258 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

