Treatment of intracranial vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 24904517
- PMCID: PMC4032992
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2014.00072
Treatment of intracranial vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
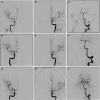
Vasospasm has been a long known source of delayed morbidity and mortality in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. Delayed ischemic neurologic deficits associated with vasospasm may account for as high as 50% of the deaths in patients who survive the initial period after aneurysm rupture and its treatment. The diagnosis and treatment of vasospasm has still been met with some controversy. It is clear that subarachnoid hemorrhage is best cared for in tertiary care centers with modern resources and access to cerebral angiography. Ultimately, a high degree of suspicion for vasospasm must be kept during ICU care, and any signs or symptoms must be investigated and treated immediately to avoid permanent stroke and neurologic deficit. Treatment for vasospasm can occur through both ICU intervention and endovascular administration of intra-arterial vasodilators and balloon angioplasty. The best outcomes are often attained when these methods are used in conjunction. The following article reviews the literature on cerebral vasospasm and its treatment and provides the authors' approach to treatment of these patients.
Keywords: balloon angioplasty; cerebral aneurysm; cerebral vasospasm; delayed ischemic neurologic deficit; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Figures
References
-
- Bederson JB, Connolly ES, Batjer HH, Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the stroke council, American heart association. Stroke (2009) 40(3):994–102510.1161/STROKEAHA.108.191395 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

