The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition
- PMID: 24905006
- PMCID: PMC4236231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.016
The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition
Abstract
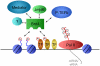
The bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) protein Brd4 recruits transcriptional regulatory complexes to acetylated chromatin. While Brd4 is considered to be a general transcriptional regulator, pharmacological inhibition of BET proteins shows therapeutic activity in a variety of different pathologies, particularly in models of cancer and inflammation. Such effects have been attributed to a specific set of downstream target genes whose expression is disproportionately sensitive to pharmacological targeting of BET proteins. Emerging evidence links the transcriptional consequences of BET inhibition to the association of Brd4 with enhancer elements, which tend to be involved in lineage-specific gene regulation. Furthermore, Brd4 engages in direct regulatory interactions with several DNA-binding transcription factors to influence their disease-relevant functions. Here we review the current understanding of molecular mechanisms that underlie the promising therapeutic effects of BET bromodomain inhibition.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bandukwala HS, Gagnon J, Togher S, Greenbaum JA, Lamperti ED, Parr NJ, Molesworth AM, Smithers N, Lee K, Witherington J, et al. Selective inhibition of CD4+ T-cell cytokine production and autoimmunity by BET protein and c-Myc inhibitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109:14532–14537. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

