Molecular control of induced pluripotency
- PMID: 24905163
- PMCID: PMC4112734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.05.002
Molecular control of induced pluripotency
Abstract
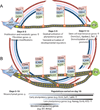
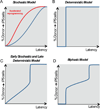
Deciphering the mechanisms of epigenetic reprogramming provides fundamental insights into cell fate decisions, which in turn reveal strategies to make the reprogramming process increasingly efficient. Here we review recent advances in epigenetic reprogramming to pluripotency with a focus on the principal molecular regulators. We examine the trajectories connecting somatic and pluripotent cells, genetic and chemical methodologies for inducing pluripotency, the role of endogenous master transcription factors in establishing the pluripotent state, and functional interactions between reprogramming factors and epigenetic regulators. Defining the crosstalk among the diverse molecular actors implicated in cellular reprogramming presents a major challenge for future inquiry.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Brons IG, Smithers LE, Trotter MW, Rugg-Gunn P, Sun B, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Howlett SK, Clarkson A, Ahrlund-Richter L, Pedersen RA, et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448:191–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

