Prediction of postoperative mortality in liver transplantation in the era of MELD-based liver allocation: a multivariate analysis
- PMID: 24905210
- PMCID: PMC4048202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098782
Prediction of postoperative mortality in liver transplantation in the era of MELD-based liver allocation: a multivariate analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: Liver transplantation is the only curative treatment for end-stage liver disease. While waiting list mortality can be predicted by the MELD-score, reliable scoring systems for the postoperative period do not exist. This study's objective was to identify risk factors that contribute to postoperative mortality.
Methods: Between December 2006 and March 2011, 429 patients underwent liver transplantation in our department. Risk factors for postoperative mortality in 266 consecutive liver transplantations were identified using univariate and multivariate analyses. Patients who were <18 years, HU-listings, and split-, living related, combined or re-transplantations were excluded from the analysis. The correlation between number of risk factors and mortality was analyzed.
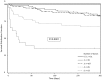
Results: A labMELD ≥20, female sex, coronary heart disease, donor risk index >1.5 and donor Na+>145 mmol/L were identified to be independent predictive factors for postoperative mortality. With increasing number of these risk-factors, postoperative 90-day and 1-year mortality increased (0-1: 0 and 0%; 2: 2.9 and 17.4%; 3: 5.6 and 16.8%; 4: 22.2 and 33.3%; 5-6: 60.9 and 66.2%).
Conclusions: In this analysis, a simple score was derived that adequately identified patients at risk after liver transplantation. Opening a discussion on the inclusion of these parameters in the process of organ allocation may be a worthwhile venture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Merion RM (2010) Current status and future of liver transplantation. Semin Liver Dis 30: 411–421. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins RL, Fairchild RB (1989) The role of transplantation in liver disease. Surg Clin North Am 69: 371–382. - PubMed
-
- Schmied BM, Mehrabi A, Schallert C, Schemmer P, Sauer P, et al. (2005) Evolution of liver transplantation at the University of Heidelberg: interventions influencing patient referral. Transplantation 80: S147–150. - PubMed
-
- Desschans B, Van Gelder F, Van Hees D, de Rocy J, Monbaliu D, et al. (2008) Evolution in allocation rules for renal, hepatic, pancreatic and intestinal grafts. Acta Chir Belg 108: 31–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

