A new Child-Turcotte-Pugh class 0 for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: determinants, prognostic impact and ability to improve the current staging systems
- PMID: 24906132
- PMCID: PMC4048310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099115
A new Child-Turcotte-Pugh class 0 for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: determinants, prognostic impact and ability to improve the current staging systems
Abstract
Background/aim: Majority of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) belonged to Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) class A. We aimed to identify a new class of patients with very well-preserved liver function and analyze its impact on outcome prediction, tumor staging and treatment allocation.
Methods: A total of 2654 HCC patients were retrospectively analyzed. The prognostic ability was compared by the Akaike information criterion (AIC).
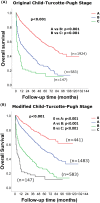
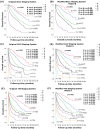
Results: The CTP class 0 was defined by fulfilling all criteria of albumin ≧4 g/dL, bilirubin ≦0.8 mg/dL, prothrombin time prolongation <0 seconds, no ascites and encephalopathy. A total of 23% of patients of CTP class A were reclassified as CTP class 0. Patients with CTP class 0 had a higher serum sodium level, lower serum creatinine, alanine aminotransferase, α-fetoprotein levels, shorter prothrombin time, better general well-being, smaller tumor burden with more solitary nodules, lower rates of vascular invasion, ascites formation, hepatic encephalopathy, more frequently treated with curative interventions and better Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages (all p<0.001). In the Cox proportional hazards model, the adjusted hazard ratios for CTP class A, B and C were 1.739, 3.120 and 5.107, respectively, compared to class 0 (all p<0.001). Reassigning patients with CTP class 0, A, B, B and C to stage 0, A, B, C and D, respectively, provided the lowest AIC score among all BCLC-based models.
Conclusions: The proposal of CTP class 0 independently predicted better survival in HCC patients. Modification of tumor staging systems according to the modified CTP classification further enhances their prognostic ability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R (2004) Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 127: S5–S16. - PubMed
-
- Child CG, Turcotte JG (1964) Surgery and portal hypertension. In: The liver and portal hypertension. Edited by CG Child. Philadelphia: Saunders 50–64.
-
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60: 646–649. - PubMed
-
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology 28: 751–755. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J (2004) The Barcelona approach: diagnosis, staging, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl 10: S115–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

