Increased adipocyte O2 consumption triggers HIF-1α, causing inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity
- PMID: 24906151
- PMCID: PMC4114226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.012
Increased adipocyte O2 consumption triggers HIF-1α, causing inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity
Abstract
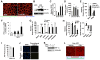
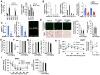
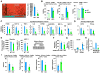
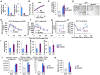
Adipose tissue hypoxia and inflammation have been causally implicated in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Here, we report that, early in the course of high-fat diet (HFD) feeding and obesity, adipocyte respiration becomes uncoupled, leading to increased oxygen consumption and a state of relative adipocyte hypoxia. These events are sufficient to trigger HIF-1α induction, setting off the chronic adipose tissue inflammatory response characteristic of obesity. At the molecular level, these events involve saturated fatty acid stimulation of the adenine nucleotide translocase 2 (ANT2), an inner mitochondrial membrane protein, which leads to the uncoupled respiratory state. Genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of either ANT2 or HIF-1α can prevent or reverse these pathophysiologic events, restoring a state of insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. These results reveal the sequential series of events in obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures



References
-
- Andreyev A, Bondareva TO, Dedukhova VI, Mokhova EN, Skulachev VP, Volkov NI. Carboxyatractylate inhibits the uncoupling effect of free fatty acids. FEBS letters. 1988;226:265–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24HD050837/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG043120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 092738/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG043120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK-063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050837/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK054441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101395/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

