The conformational and subcellular compartmental dance of plant NLRs during viral recognition and defense signaling
- PMID: 24906192
- PMCID: PMC4596408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.05.003
The conformational and subcellular compartmental dance of plant NLRs during viral recognition and defense signaling
Abstract
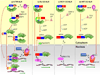
Plant innate immune response against viruses utilizes intracellular Nucleotide Binding domain Leucine Rich Repeat (NLR) class of receptors. NLRs recognize different viral proteins termed elicitors and initiate diverse signaling processes that induce programmed cell death (PCD) in infected cells and restrict virus spread. In this review we describe the recent advances made in the study of plant NLRs that detect viruses. We describe some of the physical and functional interactions these NLRs undertake. We elaborate on the intra-molecular and homotypic association of NLRs that function in self-regulation and activation. Nuclear role for some viral NLRs is discussed as well as the emerging importance of the RNAi pathway in regulating the NLR family.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pumplin N, Voinnet O. RNA silencing suppression by plant pathogens: defence, counter-defence and counter-counter-defence. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:745–760. - PubMed
-
- Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B. The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell. 1994;78:1101–1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

