Microfluidic techniques for development of 3D vascularized tissue
- PMID: 24906345
- PMCID: PMC4118596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.091
Microfluidic techniques for development of 3D vascularized tissue
Abstract
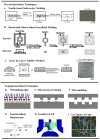
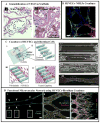
Development of a vascularized tissue is one of the key challenges for the successful clinical application of tissue engineered constructs. Despite the significant efforts over the last few decades, establishing a gold standard to develop three dimensional (3D) vascularized tissues has still remained far from reality. Recent advances in the application of microfluidic platforms to the field of tissue engineering have greatly accelerated the progress toward the development of viable vascularized tissue constructs. Numerous techniques have emerged to induce the formation of vascular structure within tissues which can be broadly classified into two distinct categories, namely (1) prevascularization-based techniques and (2) vasculogenesis and angiogenesis-based techniques. This review presents an overview of the recent advancements in the vascularization techniques using both approaches for generating 3D vascular structure on microfluidic platforms.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Microfluidics; Micromolding; Tissue engineering; Vascularization; Vasculogenesis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Du Y, Cropek D, Mofrad MRK, Weinberg EJ, Khademhosseinil A, Borenstein J. Microfluidic systems for engineering vascularized tissue constructs. In: Tian W-C, Finehout E, editors. Microfluidics for Biological Applications. New York: Springer; 2008.
-
- Kaully T, Kaufman-Francis K, Lesman A, Levenberg S. Vascularization - the conduit to viable engineered tissues. Tissue Eng Pt B: Rev. 2009;15:159–69. - PubMed
-
- Hasan A, Ragaert K, Swieszkowski W, Selimović Š, Paul A, Camci-Unal G, et al. Biomechanical properties of native and tissue engineered heart valve constructs. J Biomech. 2013 In press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EB012597/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- HL092836/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EB012597/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- DE019024/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092836/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EB008392/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- DE021468/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021468/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- HL099073/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057837/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL099073/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR057837/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DE019024/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008392/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

