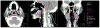Late radiation-associated dysphagia (late-RAD) with lower cranial neuropathy after oropharyngeal radiotherapy: a preliminary dosimetric comparison
- PMID: 24906528
- PMCID: PMC4158823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.05.003
Late radiation-associated dysphagia (late-RAD) with lower cranial neuropathy after oropharyngeal radiotherapy: a preliminary dosimetric comparison
Abstract
Background and objectives: Late radiation-associated dysphagia (late-RAD) is a rare delayed toxicity, in oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) survivors. Prevention of late-RAD is paramount because the functional impairment can be profound and refractory to standard therapies. The objective of this analysis is to identify candidate dosimetric predictors of late-RAD and associated lower cranial neuropathies after radiotherapy (RT) or chemo-RT (CRT) for OPC.
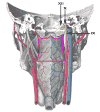
Materials and methods: An unmatched retrospective case-control analysis was conducted. Late-RAD cases were identified among OPC patients treated with definitive RT or CRT. Controls were selected with minimum of 6 years without symptoms of late-RAD. Dysphagia-aspiration related structures (DARS) and regions of interest containing cranial nerve paths (RCCNPs) were retrospectively contoured. Dose volume histograms were calculated. Non-parametric bivariate associations were analyzed with Bonferroni correction and multiple logistic regression models were fit.
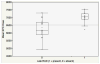
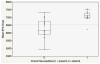
Results: Thirty-eight patients were included (12 late-RAD cases, 26 controls). Median latency to late-RAD was 5.8 years (range: 4.5-11.3 years). Lower cranial neuropathies were present in 10 of 12 late-RAD cases. Mean superior pharyngeal constrictor (SPC) dose was higher in cases relative to controls (median: 70.5 vs. 61.6 Gy). Mean SPC dose significantly predicted late-RAD (p = 0.036) and related cranial neuropathies (p = 0.019). RCCNPs did not significantly predict late-RAD or cranial neuropathies.
Conclusions: SPC dose may predict for late-RAD and related lower cranial neuropathies. These data, and those of previous studies that have associated SPC dose with classical dysphagia endpoints, suggest impetus to constrain dose to the SPCs when possible.
Keywords: Dysphagia; Oropharyngeal cancer; Pharyngeal constrictors; Quality-of-life; Radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenthal DI, Lewin JS, Eisbruch A. Prevention and treatment of dysphagia and aspiration after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2636–2643. - PubMed
-
- Sanguineti G, Gunn GB, Parker BC, Endres EJ, Zeng J, Fiorino C. Weekly dose-volume parameters of mucosa and constrictor muscles predict the use of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy during exclusive intensity-modulated radiotherapy for oropharyngeal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Starmer H, Alcorn E, Murano YL, Quon H. Radiation dose to the floor of mouth muscles predicts swallowing complications after chemoradiation in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;84:S206–S207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials