Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: recent advances in the understanding of the pivotal role of inflammation, risk predictors and the impact of treatment
- PMID: 24907149
- PMCID: PMC4241890
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu224
Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: recent advances in the understanding of the pivotal role of inflammation, risk predictors and the impact of treatment
Abstract
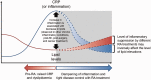
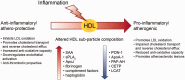
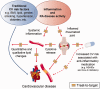
Risk of cardiovascular (CV) disease is increased among RA patients. High inflammatory burden associated with RA appears to be a key driver of the increased cardiovascular risk. Inflammation is linked with accelerated atherosclerosis and associated with a paradoxical inversion of the relationship between CV risk and lipid levels in patients with untreated RA, recently coined the lipid paradox. Furthermore, the inflammatory burden is also associated with qualitative as well as quantitative changes in lipoproteins, with the anti-inflammatory and atheroprotective roles associated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol significantly altered. RA therapies can increase lipid levels, which may reflect the normalization of lipids due to their inflammatory-dampening effects. However, these confounding influences of inflammation and RA therapies on lipid profiles pose challenges for assessing CV risk in RA patients and interpretation of traditional CV risk scores. In this review we examine the relationship between the increased inflammatory burden in RA and CV risk, exploring how inflammation influences lipid profiles, the impact of RA therapies and strategies for identifying and monitoring CV risk in RA patients aimed at improving CV outcomes.
Keywords: anti-rheumatic agents; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; dyslipidaemias; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Peters MJ, Symmons DP, McCarey D, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:325–31. - PubMed
-
- Meune C, Touze E, Trinquart L, Allanore Y. Trends in cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 50 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology. 2009;48:1309–13. - PubMed
-
- Avina-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, et al. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1690–7. - PubMed
-
- Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation. 2003;107:1303–7. - PubMed
-
- de Groot L, Posthumus MD, Kallenberg CG, Bijl M. Risk factors and early detection of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40:835–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

