Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of lupus
- PMID: 24907379
- PMCID: PMC4083591
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002795
Type I interferon in the pathogenesis of lupus
Abstract
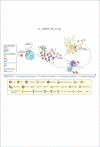
Investigations of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have applied insights from studies of the innate immune response to define IFN-I, with IFN-α as the dominant mediator, as central to the pathogenesis of this prototype systemic autoimmune disease. Genetic association data identify regulators of nucleic acid degradation and components of TLR-independent, endosomal TLR-dependent, and IFN-I-signaling pathways as contributors to lupus disease susceptibility. Together with a gene expression signature characterized by IFN-I-induced gene transcripts in lupus blood and tissue, those data support the conclusion that many of the immunologic and pathologic features of this disease are a consequence of a persistent self-directed immune reaction driven by IFN-I and mimicking a sustained antivirus response. This expanding knowledge of the role of IFN-I and the innate immune response suggests candidate therapeutic targets that are being tested in lupus patients.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, Harley JB. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1526–1533. - PubMed
-
- Lerner EA, Lerner MR, Hardin JA, Janeway CA, Jr., Steitz JA. Deciphering the mysteries of RNA-containing lupus antigens. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:761–766. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi T, Abe T, Koide J, Hosono O, Morimoto C, Homma M. Cellular mechanism of DNA-specific antibody synthesis by lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27:766–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

