Expression, purification and reconstitution of the 4-hydroxybenzoate transporter PcaK from Acinetobacter sp. ADP1
- PMID: 24907408
- PMCID: PMC4148202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.05.011
Expression, purification and reconstitution of the 4-hydroxybenzoate transporter PcaK from Acinetobacter sp. ADP1
Abstract
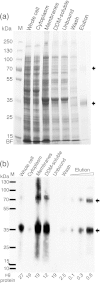
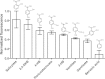
The aromatic acid:H(+) symporter family of integral membrane proteins play an important role in the microbial metabolism of aromatic compounds. Here, we show that the 4-hydroxybenzoate transporter from Acinetobacter sp. ADP1, PcaK, can be successfully overexpressed in Escherichia coli and purified by affinity chromatography. Affinity-purified PcaK is a stable, monodisperse homotrimer in the detergent n-dodecyl-β-d-maltopyranoside supplemented with cholesteryl hemisuccinate. The purified protein has α-helical secondary structure and can be reconstituted to a functional state in synthetic proteoliposomes. Asymmetric substrate transport was observed when proteoliposomes were energized by applying an electrochemical proton gradient (Δμ‾H(+)) or a membrane potential (ΔΨ) but not by ΔpH alone. PcaK was selective in transporting 4-hydroxybenzoate and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate over closely related compounds, confirming previous reports on substrate specificity. However, PcaK also showed an unexpected preference for transporting 2-hydroxybenzoates. These results provide the basis for further detailed studies of the structure and function of this family of transporters.
Keywords: Enzyme purification; Membrane proteins; Membrane transport; Recombinant protein expression; Reconstitution of membrane transporters.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures









References
-
- Gibson D.T., Parales R.E. Aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenases in environmental biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000;11:236–243. - PubMed
-
- Cao B., Nagarajan K., Loh K.-C. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009;85:207–228. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs G., Boll M., Heider J. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds – from one strategy to four. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011;9:803–816. - PubMed
-
- Kirk T.K., Farrell R.L. Enzymatic “combustion”: the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987;41:465–505. - PubMed
-
- Bugg T.D.H., Ahmad M., Hardiman E.M., Rahmanpour R. Pathways for degradation of lignin in bacteria and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011;28:1883–1896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

