Role for β-arrestin in mediating paradoxical β2AR and PAR2 signaling in asthma
- PMID: 24907413
- PMCID: PMC4116123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2014.03.007
Role for β-arrestin in mediating paradoxical β2AR and PAR2 signaling in asthma
Abstract
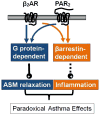
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) utilize (at least) two signal transduction pathways to elicit cellular responses including the classic G protein-dependent, and the more recently discovered β-arrestin-dependent, signaling pathways. In human and murine models of asthma, agonist-activation of β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) or Protease-activated-receptor-2 (PAR2) results in relief from bronchospasm via airway smooth muscle relaxation. However, chronic activation of these receptors, leads to pro-inflammatory responses. One plausible explanation underlying the paradoxical effects of β2AR and PAR2 agonism in asthma is that the beneficial and harmful effects are associated with distinct signaling pathways. Specifically, G protein-dependent signaling mediates relaxation of airway smooth muscle, whereas β-arrestin-dependent signaling promotes inflammation. This review explores the evidence supporting the hypothesis that β-arrestin-dependent signaling downstream of β2AR and PAR2 is detrimental in asthma and examines the therapeutic opportunities for selectively targeting this pathway.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- (NAEPP) NAEaPP: Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma–Summary Report 2007. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2007;120:S94–S138. - PubMed
-
- Nichols HL, Saffeddine M, Theriot BS, Hegde A, Polley D, El-Mays T, Vliagoftis H, Hollenberg MD, Wilson EH, Walker JKL, et al. β-Arrestin-2 mediates the proinflammatory effects of proteinase-activated receptor-2 in the airway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2012;109:16660–16665. This study demonstrates that unbiased PAR2 ligands mediate protective bronchorelaxation and deleterious inflammation via the G protein-dependent and β-arrestin-dependent signaling pathways, respectively, in an antigen-driven murine asthma model. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Whalen EJ. [beta]-arrestins: traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:162–168. - PubMed

