Role of soluble adenylyl cyclase in mitochondria
- PMID: 24907564
- PMCID: PMC4257896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.035
Role of soluble adenylyl cyclase in mitochondria
Abstract
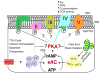
The soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC) catalyzes the conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP). Recent studies have shed new light on the role of sAC localized in mitochondria and its product cAMP, which drives mitochondrial protein phosphorylation and regulation of the oxidative phosphorylation system and other metabolic enzymes, presumably through the activation of intra-mitochondrial PKA. In this review article, we summarize recent findings on mitochondrial sAC activation by bicarbonate (HCO(3)(-)) and calcium (Ca²⁺) and the effects on mitochondrial metabolism. We also discuss putative mechanisms whereby sAC-mediated mitochondrial protein phosphorylation regulates mitochondrial metabolism. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: The role of soluble adenylyl cyclase in health and disease.
Keywords: Mitochondria; PKA; Protein phosphorylation; cAMP; sAC.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Braun T. The effect of divalent cations on bovine spermatozoal adenylate cyclase activity. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Cann MJ, Litvin TN, Iourgenko V, Sinclair ML, Levin LR, Buck J. Soluble adenylyl cyclase as an evolutionarily conserved bicarbonate sensor. Science. 2000;289:625–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

