Final report of the phase I/II clinical trial of the E75 (nelipepimut-S) vaccine with booster inoculations to prevent disease recurrence in high-risk breast cancer patients
- PMID: 24907636
- PMCID: PMC4143091
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdu211
Final report of the phase I/II clinical trial of the E75 (nelipepimut-S) vaccine with booster inoculations to prevent disease recurrence in high-risk breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: E75 (nelipepimut-S) is a human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2/A3-restricted immunogenic peptide derived from the HER2 protein. We have conducted phase I/II clinical trials vaccinating breast cancer patients with nelipepimut-S and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in the adjuvant setting to prevent disease recurrence. All patients have completed 60 months follow-up, and here, we report the final analyses.
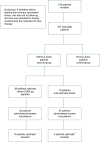
Patients and methods: The studies were conducted as dose escalation/schedule optimization trials enrolling node-positive and high-risk node-negative patients with tumors expressing any degree of HER2 (immunohistochemistry 1-3+). HLA-A2/3+ patients were vaccinated; others were followed prospectively as controls. Local and systemic toxicity was monitored. Clinical recurrences were documented, and disease-free survival (DFS) was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier curves; groups were compared using log-rank tests.
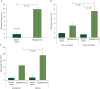
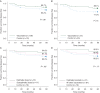
Results: Of 195 enrolled patients, 187 were assessable: 108 (57.8%) in the vaccinated group (VG) and 79 (42.2%) in the control group (CG). The groups were well matched for clinicopathologic characteristics. Toxicities were minimal. Five-year DFS was 89.7% in the VG versus 80.2% in the CG (P = 0.08). Due to trial design, 65% of patients received less than the optimal vaccine dose. Five-year DFS was 94.6% in optimally dosed patients (P = 0.05 versus the CG) and 87.1% in suboptimally dosed patients. A voluntary booster program was initiated, and among the 21 patients that were optimally boosted, there was only one recurrence (DFS = 95.2%).
Conclusion: The E75 vaccine is safe and appears to have clinical efficacy. A phase III trial evaluating the optimal dose and including booster inoculations has been initiated.
Clinical trials: NCT00841399, NCT00584789.
Keywords: breast cancer; immunotherapy; nelipepimut-S; vaccine.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Breast cancer: E75-a safe and effective vaccine for the prevention of disease recurrence.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Aug;11(8):440. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.110. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24958184 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brossart P, Wirths S, Stuhler G, et al. Induction of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in vivo after vaccinations with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Blood. 2000;96:3102–3108. - PubMed
-
- Disis ML, Gooley TA, Rinn K, et al. Generation of T-cell immunity to the HER-2/neu protein after active immunization with HER-2/neu peptide-based vaccines. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2624–2632. - PubMed
-
- Knutson KL, Schiffman K, Cheever MA, Disis ML. Immunization of cancer patients with a HER-2/neu, HLA-A2 peptide, p369–377, results in short-lived peptide-specific immunity. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1014–1018. - PubMed
-
- Zaks TZ, Rosenberg SA. Immunization with a peptide epitope (p369–377) from HER-2/neu leads to peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes that fail to recognize HER-2/neu+ tumors. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4902–4908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

