Acupuncture for acute stroke: study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 24908241
- PMCID: PMC4057817
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-214
Acupuncture for acute stroke: study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture has been widely used as a treatment for stroke in China for more than 3,000 years. However, previous research has not yet shown that acupuncture is effective as a stroke treatment. We report a protocol for a multicenter, randomized, controlled, and outcome assessor-blind trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acupuncture on acute ischemic stroke.
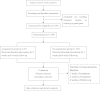
Methods/design: In a prospective trial involving three hospitals in the Zhejiang Province (China) 250 patients with a recent (less than 1 week previous) episode of ischemic stroke will be included. Patients will be randomized into two groups: an acupuncture group given scalp acupuncture and electroacupuncture, and a control group given no acupuncture. Eighteen treatment sessions will be performed over a three-week period. The primary outcome will be measured by changes in the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score at the one, three, and four-week follow-up. Secondary outcome measures will be: 1) the Fugl-Meyer assessment scale for motor function; 2) the mini-mental state examination and Montreal cognitive assessment for cognitive function; 3) the video-fluoroscopic swallowing study for swallowing ability; and 4) the incidence of adverse events.
Discussion: This trial is expected to clarify whether or not acupuncture is effective for acute stroke. It will also show if acupuncture can improve motor, cognitive, or swallowing function.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry ChiCTR-TRC-12001971.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical