Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery
- PMID: 24909511
- PMCID: PMC4571323
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.18
Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery
Abstract
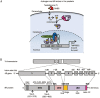
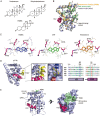
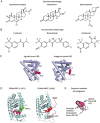
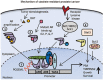
Androgens and androgen receptors (AR) play a pivotal role in expression of the male phenotype. Several diseases, such as androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) and prostate cancer, are associated with alterations in AR functions. Indeed, androgen blockade by drugs that prevent the production of androgens and/or block the action of the AR inhibits prostate cancer growth. However, resistance to these drugs often occurs after 2-3 years as the patients develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). In CRPC, a functional AR remains a key regulator. Early studies focused on the functional domains of the AR and its crucial role in the pathology. The elucidation of the structures of the AR DNA binding domain (DBD) and ligand binding domain (LBD) provides a new framework for understanding the functions of this receptor and leads to the development of rational drug design for the treatment of prostate cancer. An overview of androgen receptor structure and activity, its actions in prostate cancer, and how structural information and high-throughput screening have been or can be used for drug discovery are provided herein.
Figures


References
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem 1994; 63: 451–86. - PubMed
-
- Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee. A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily. Cell 1999; 97: 161–3. - PubMed
-
- Rosner W, Hryb DJ, Khan MS, Nakhla AM, Romas NA. Sex hormone-binding globulin: anatomy and physiology of a new regulatory system. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1991; 40: 813–20. - PubMed
-
- Baker ME. Albumin, steroid hormones and the origin of vertebrates. J Endocrinol 2002; 175: 121–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

