Evaluation of an immunoassay for determination of plasma efavirenz concentrations in resource-limited settings
- PMID: 24909561
- PMCID: PMC4049128
- DOI: 10.7448/IAS.17.1.18979
Evaluation of an immunoassay for determination of plasma efavirenz concentrations in resource-limited settings
Abstract
Introduction: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) may improve antiretroviral efficacy through adjustment of individual drug administration. This could result in reduced toxicity, prevent drug resistance, and aid management of drug-drug interactions. However, most measurement methods are too costly to be implemented in resource-limited settings. This study evaluated a commercially available immunoassay for measurement of plasma efavirenz.
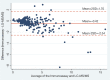
Methods: The immunoassay-based method was applied to measure efavirenz using a readily available Humastar 80 chemistry analyzer. We compared plasma efavirenz concentrations measured by the immunoassay with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) (reference method) in 315 plasma samples collected from HIV patients on treatment. Concentrations were categorized as suboptimal<1 µg/ml, normal 1-4 µg/ml or high>4 µg/ml. Agreement between results of the methods was assessed via Bland-Altman plot and κ statistic values.
Results: The median Interquartile range (IQR) efavirenz concentration was 2.8 (1.9; 4.5) µg/ml measured by the LC-MS/MS method and 2.5 (1.8; 3.9) µg/ml by the immunoassay and the results were well correlated (ρ=0.94). The limits of agreement assessed by Bland-Altman plots were -2.54; 1.70 µg/ml. Although immunoassay underestimated high concentrations, it had good agreement for classification into low, normal or high concentrations (K=0.74).
Conclusions: The immunoassay is a feasible alternative to determine efavirenz in areas with limited resources. The assay provides a reasonable approximation of efavirenz concentration in the majority of samples with a tendency to underestimate high concentrations. Agreement between tests evaluated in this study was clinically satisfactory for identification of low, normal and high efavirenz concentrations.
Keywords: LC–MS/MS; TDM; antiretroviral therapy; efavirenz; immunoassay; method evaluation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A validated method for simultaneous quantification of four antiretrovirals in dried blood spot and plasma using LC-MS/MS: Application to efavirenz therapeutic drug monitoring in pregnant patients.Clin Biochem. 2024 May;127-128:110765. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2024.110765. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Clin Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38649089
-
A sensitive and selective liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for quantitative analysis of efavirenz in human plasma.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 5;8(6):e63305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063305. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755102 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Efavirenz Hydroxymetabolites in Human Plasma Using LC-HRMS/MS.Ther Drug Monit. 2024 Aug 1;46(4):468-476. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000001173. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Ther Drug Monit. 2024. PMID: 38864581
-
Efavirenz concentrations in CSF exceed IC50 for wild-type HIV.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Feb;66(2):354-7. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq434. Epub 2010 Nov 23. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21098541 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pharmacogenetic markers of CYP2B6, clinical factors, and drug-drug interaction on efavirenz concentrations in HIV/tuberculosis-coinfected patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Feb;57(2):1019-24. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02023-12. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23254426 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma nevirapine concentrations predict virological and adherence failure in Kenyan HIV-1 infected patients with extensive antiretroviral treatment exposure.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 24;12(2):e0172960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172960. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28235021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luetkemeyer AF, Rosenkranz SL, Lu D, Marzan F, Ive P, Hogg E, et al. Relationship between weight, efavirenz exposure, and virologic suppression in HIV-infected patients on rifampin-based tuberculosis treatment in the AIDS Clinical Trials Group A5221 STRIDE Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57(4):586–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Protopopescu C, Raffi F, Roux P, Reynes J, Dellamonica P, Spire B, et al. Factors associated with non-adherence to long-term highly active antiretroviral therapy: a 10 year follow-up analysis with correction for the bias induced by missing data. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;64(3):599–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical