Crystal structure of a human GABAA receptor
- PMID: 24909990
- PMCID: PMC4167603
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13293
Crystal structure of a human GABAA receptor
Abstract
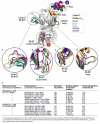
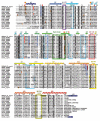
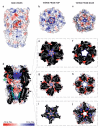
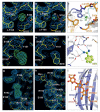
Type-A γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABAARs) are the principal mediators of rapid inhibitory synaptic transmission in the human brain. A decline in GABAAR signalling triggers hyperactive neurological disorders such as insomnia, anxiety and epilepsy. Here we present the first three-dimensional structure of a GABAAR, the human β3 homopentamer, at 3 Å resolution. This structure reveals architectural elements unique to eukaryotic Cys-loop receptors, explains the mechanistic consequences of multiple human disease mutations and shows an unexpected structural role for a conserved N-linked glycan. The receptor was crystallized bound to a previously unknown agonist, benzamidine, opening a new avenue for the rational design of GABAAR modulators. The channel region forms a closed gate at the base of the pore, representative of a desensitized state. These results offer new insights into the signalling mechanisms of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels and enhance current understanding of GABAergic neurotransmission.
Figures





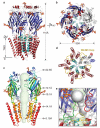





References
-
- Rabow LE, Russek SJ, Farb DH. From ion currents to genomic analysis: recent advances in GABAA receptor research. Synapse. 1995;21:189–274. - PubMed
-
- Grenningloh G, et al. Glycine vs GABA receptors. Nature. 1987;330:25–26. - PubMed
-
- Simon J, Wakimoto H, Fujita N, Lalande M, Barnard EA. Analysis of the set of GABA(A) receptor genes in the human genome. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:41422–41435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

