Delayed fracture healing and increased callus adiposity in a C57BL/6J murine model of obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24911161
- PMCID: PMC4049817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099656
Delayed fracture healing and increased callus adiposity in a C57BL/6J murine model of obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: Impaired healing and non-union of skeletal fractures is a major public health problem, with morbidity exacerbated in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). DM is prevalent worldwide and affects approximately 25.8 million US adults, with >90% having obesity-related type 2 DM (T2DM). While fracture healing in type 1 DM (T1DM) has been studied using animal models, an investigation into delayed healing in an animal model of T2DM has not yet been performed.
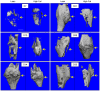
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mice at 5 weeks of age were placed on either a control lean diet or an experimental high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks. A mid-diaphyseal open tibia fracture was induced at 17 weeks of age and a spinal needle was used for intra-medullary fixation. Mice were sacrificed at days 7, 10, 14, 21, 28, and 35 for micro-computed tomography (μCT), histology-based histomorphometry and molecular analyses, and biomechanical testing.
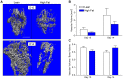
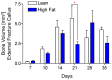
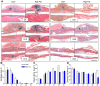
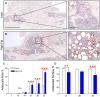
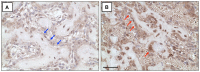
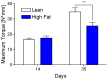
Results: HFD-fed mice displayed increased body weight and impaired glucose tolerance, both characteristic of T2DM. Compared to control mice, HFD-fed mice with tibia fractures showed significantly (p<0.001) decreased woven bone at day 28 by histomorphometry and significantly (p<0.01) decreased callus bone volume at day 21 by μCT. Interestingly, fracture calluses contained markedly increased adiposity in HFD-fed mice at days 21, 28, and 35. HFD-fed mice also showed increased PPARγ immunohistochemical staining at day 14. Finally, calluses from HFD-fed mice at day 35 showed significantly (p<0.01) reduced torsional rigidity compared to controls.
Discussion: Our murine model of T2DM demonstrated delayed fracture healing and weakened biomechanical properties, and was distinctly characterized by increased callus adiposity. This suggests altered mesenchymal stem cell fate determination with a shift to the adipocyte lineage at the expense of the osteoblast lineage. The up-regulation of PPARγ in fracture calluses of HFD-fed mice is likely involved in the proposed fate switching.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Alarcon T, Gonzalez-Montalvo JI, Gotor P, Madero R, Otero A (2011) Activities of daily living after hip fracture: profile and rate of recovery during 2 years of follow-up. Osteoporos Int 22: 1609–1613. - PubMed
-
- Brenneman SK, Barrett-Connor E, Sajjan S, Markson LE, Siris ES (2006) Impact of recent fracture on health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 21: 809–816. - PubMed
-
- Ding R, McCarthy ML, Houseknecht E, Ziegfeld S, Knight VM, et al. (2006) The health-related quality of life of children with an extremity fracture: a one-year follow-up study. J Pediatr Orthop 26: 157–163. - PubMed
-
- Giannoudis PV, Harwood PJ, Kontakis G, Allami M, Macdonald D, et al. (2009) Long-term quality of life in trauma patients following the full spectrum of tibial injury (fasciotomy, closed fracture, grade IIIB/IIIC open fracture and amputation). Injury 40: 213–219. - PubMed
-
- Lonnroos E, Kautiainen H, Sund R, Karppi P, Hartikainen S, et al. (2009) Utilization of inpatient care before and after hip fracture: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int 20: 879–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

