ABCC transporters mediate insect resistance to multiple Bt toxins revealed by bulk segregant analysis
- PMID: 24912445
- PMCID: PMC4071345
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-46
ABCC transporters mediate insect resistance to multiple Bt toxins revealed by bulk segregant analysis
Abstract
Background: Relatively recent evidence indicates that ABCC2 transporters play a main role in the mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry1A-type proteins. Mapping of major Cry1A resistance genes has linked resistance to the ABCC2 locus in Heliothis virescens, Plutella xylostella, Trichoplusia ni and Bombyx mori, and mutations in this gene have been found in three of these Bt-resistant strains.
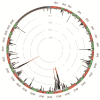
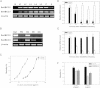
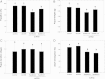
Results: We have used a colony of Spodoptera exigua (Xen-R) highly resistant to a Bt commercial bioinsecticide to identify regions in the S. exigua genome containing loci for major resistance genes by using bulk segregant analysis (BSA). Results reveal a region containing three genes from the ABCC family (ABBC1, ABBC2 and ABBC3) and a mutation in one of them (ABBC2) as responsible for the resistance of S. exigua to the Bt commercial product and to its key Spodoptera-active ingredients, Cry1Ca. In contrast to all previously described mutations in ABCC2 genes that directly or indirectly affect the extracellular domains of the membrane protein, the ABCC2 mutation found in S. exigua affects an intracellular domain involved in ATP binding. Functional analyses of ABBC2 and ABBC3 support the role of both proteins in the mode of action of Bt toxins in S. exigua. Partial silencing of these genes with dsRNA decreased the susceptibility of wild type larvae to both Cry1Ac and Cry1Ca. In addition, reduction of ABBC2 and ABBC3 expression negatively affected some fitness components and induced up-regulation of arylphorin and repat5, genes that respond to Bt intoxication and that are found constitutively up-regulated in the Xen-R strain.
Conclusions: The current results show the involvement of different members of the ABCC family in the mode of action of B. thuringiensis proteins and expand the role of the ABCC2 transporter in B. thuringiensis resistance beyond the Cry1A family of proteins to include Cry1Ca.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar S, Chandra A, Pandey KC. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) transgenic crop: an environment friendly insect-pest management strategy. J Environ Biol. 2008;12:641–653. - PubMed
-
- Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P. Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011;12:283–300. - PubMed
-
- Ferré J, Van Rie J, MacIntosh SC. In: Integration of Insect-resistant Genetically Modified Crops within IPM Programs. Romeis J, Shelton AM, Kennedy GG, editor. Dordrecht: Springer Science and Business Media; 2008. Insecticidal genetically modified crops and insect resistance management (IRM) pp. 41–85.
-
- Tabashnik BE, Brevault T, Carriere Y. Insect resistance to Bt crops: lessons from the first billion acres. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;12:510–521. - PubMed
-
- Sumerford DV, Head GP, Shelton A, Greenplate J, Moar W. Field-evolved resistance: assessing the problem and ways to move forward. J Econ Entomol. 2013;12:1525–1534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

