In vitro assessment of knee MRI in the presence of metal implants comparing MAVRIC-SL and conventional fast spin echo sequences at 1.5 and 3 T field strength
- PMID: 24912802
- PMCID: PMC4297744
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24668
In vitro assessment of knee MRI in the presence of metal implants comparing MAVRIC-SL and conventional fast spin echo sequences at 1.5 and 3 T field strength
Abstract
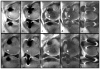
Purpose: To assess lesion detection and artifact size reduction of a multiacquisition variable-resonance image combination, slice encoding for metal artifact correction (MAVRIC-SEMAC) hybrid sequence (MAVRIC-SL) compared to standard sequences at 1.5T and 3T in porcine knee specimens with metal hardware.
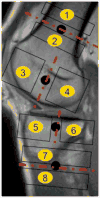
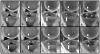
Materials and methods: Artificial cartilage and bone lesions of defined size were created in the proximity of titanium and steel screws with 2.5 mm diameter in 12 porcine knee specimens and were imaged at 1.5T and 3T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with MAVRIC-SL PD and short T1 inversion recovery (STIR), standard fast spin echo (FSE) T2 PD, and STIR and fat-saturated T2 FSE sequences. Three radiologists blinded to the lesion locations assessed lesion detection rates on randomized images for each sequence using receiver operating characteristic (ROC). Artifact length and width were measured.
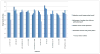
Results: Metal artifact sizes were largest in the presence of steel screws at 3T (FSE T2 FS: 28.7 cm(2) ) and 1.5T (16.03 cm(2) ). MAVRIC-SL PD and STIR reduced artifact sizes at both 3T (1.43 cm(2) ; 2.46 cm(2) ) and 1.5T (1.16 cm(2) ; 1.59 cm(2) ) compared to FS T2 FSE sequences (27.57 cm(2) ; 13.20 cm(2) ). At 3T, ROC-derived AUC values using MAVRIC-SL sequences were significantly higher compared to standard sequences (MAVRIC-PD: 0.87, versus FSE-T2 -FS: 0.73 [P = 0.025]; MAVRIC-STIR: 0.9 vs. T2 -STIR: 0.78 [P = 0.001] and vs. FSE-T2 -FS: 0.73 [P = 0.026]). Similar values were observed at 1.5T. Comparison of 3T and 1.5T showed no significant differences (MAVRIC-SL PD: P = 0.382; MAVRIC-SL STIR: P = 0.071).
Conclusion: MAVRIC-SL sequences provided superior lesion detection and reduced metal artifact size at both 1.5T and 3T compared to conventionally used FSE sequences. No significant disadvantage was found comparing MAVRIC-SL at 3T and 1.5T, although metal artifacts at 3T were larger. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015;41:1291-1299. © 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: MAVRIC-SL; artifact reduction; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); periprosthetic imaging.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
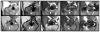
References
-
- Hayter CL, Koff MF, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging of the postoperative hip. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35(5):1013–25. - PubMed
-
- Koch KM, Lorbiecki JE, Hinks RS, King KF. A multispectral three-dimensional acquisition technique for imaging near metal implants. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61(2):381–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

