Interactions with DCAF1 and DDB1 in the CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase are required for Vpr-mediated G2 arrest
- PMID: 24912982
- PMCID: PMC4058697
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-108
Interactions with DCAF1 and DDB1 in the CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase are required for Vpr-mediated G2 arrest
Abstract
Background: HIV-1 Vpr-mediated G2 cell cycle arrest is dependent on the interaction of Vpr with an E3 ubiquitin ligase that contains damage-specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1), Cullin 4A (Cul4A), DDB1 and Cul4-associated factor 1 (DCAF1), and Rbx1. Vpr is thought to associate directly with DCAF1 in the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex although the exact interaction pattern of the proteins in the complex is not completely defined. The Vpr of SIVagm induces G2 arrest of cognate African Green Monkey (AGM) cells but not human cells. The molecular mechanism by which SIVagm Vpr exhibits its species-specific function remained unknown.
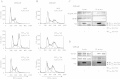
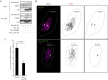
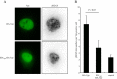
Methods: Physical interaction of proteins in the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting. In addition, co-localization of the proteins in cells was investigated by confocal microscopy. The cell cycle was analyzed by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. DNA damage response elicited by Vpr was evaluated by detecting phosphorylation of H2AX, a marker for DNA damage response.
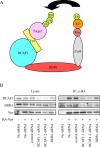
Results: We show that RNAi knock-down of DCAF1 prevented the co-immunoprecipitation of DDB1 with HIV-1 Vpr while DDB1 knock-down did not influence the binding of Vpr to DCAF1. HIV-1 Vpr mutants with a L64P or a R90K mutation maintained the ability to associate with DCAF1 but did not appear to be in a complex with DDB1. SIVagm Vpr associated with AGM DCAF1 and DDB1 while, in human cells, it binds to human DCAF1 but hardly binds to human DDB1, resulting in the reduced activation of H2AX.
Conclusions: The identification of Vpr mutants which associate with DCAF1 but only poorly with DDB1 suggests that DCAF1 is necessary but the simple binding of Vpr to DCAF1 is not sufficient for the Vpr association with DDB1-containing E3 ligase complex. Vpr may interact both with DCAF1 and DDB1 in the E3 ligase complex. Alternatively, the interaction of Vpr and DCAF1 may induce a conformational change in DCAF1 or Vpr that promotes the interaction with DDB1. The ability of SIVagm Vpr to associate with DDB1, but not DCAF1, can explain the species-specificity of SIVagm Vpr-mediated G2 arrest.
Figures

References
-
- Balliet JW, Kolson DL, Eiger G, Kim FM, McGann KA, Srinivasan A, Collman R. Distinct effects in primary macrophages and lymphocytes of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 accessory genes vpr, vpu, and nef: mutational analysis of a primary HIV-1 isolate. Virology. 1994;200:623–631. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1225. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

