Acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 24913799
- PMCID: PMC5528615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.05.003
Acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer
Abstract
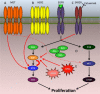
Cetuximab and panitumumab are anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR) monoclonal antibodies used as therapies for metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Intrinsic mechanisms of resistance, such as RAS mutations, can prevent patients from having a response with clinical benefit. The clinical efficacy of EGFR targeted antibodies is limited by the development of acquired (secondary) resistance, which typically occurs within 3-12 months from the start of therapy. Preclinical models and analyses of clinical samples have uncovered some of the alterations that confer a selective advantage to tumor cells when under the pressure of anti-EGFR therapy. Molecular profiling of clinical specimens confirmed that genetic alterations of genes in the EGFR-RAS-RAF-MEK signaling pathway and of receptor tyrosine kinases are mechanisms of acquired resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies. The escape from anti-EGFR blockade appears to converge on the (re)activation of MEK-ERK or AKT as revealed in preclinical studies. Circulating tumor DNA and patient derived xenografts have proven useful tools to monitor patients for resistance to anti-EGFR therapy and test combination therapies to overcome or reverse resistance.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; Anti-EGFR therapy; Cetuximab; Colorectal cancer; MET; Panitumumab; RAS.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Adam, R. , Wicherts, D.A. , de Haas, R.J. , Ciacio, O. , Lévi, F. , Paule, B. , Ducreux, M. , Azoulay, D. , Bismuth, H. , Castaing, D. , 2009. Patients with initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases: is there a possibility of cure?. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 1829–1835. - PubMed
-
- Amado, R.G. , Wolf, M. , Peeters, M. , Van Cutsem, E. , Siena, S. , Freeman, D.J. , Juan, T. , Sikorski, R. , Suggs, S. , Radinsky, R. , Patterson, S.D. , Chang, D.D. , 2008. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 1626–1634. - PubMed
-
- Bardelli, A. , Corso, S. , Bertotti, A. , Hobor, S. , Valtorta, E. , Siravegna, G. , Sartore-Bianchi, A. , Scala, E. , Cassingena, A. , Zecchin, D. , Apicella, M. , Migliardi, G. , Galimi, F. , Lauricella, C. , Zanon, C. , Perera, T. , Veronese, S. , Corti, G. , Amatu, A. , Gambacorta, M. , Diaz, L.A. , Sausen, M. , Velculescu, V.E. , Comoglio, P. , Trusolino, L. , Di Nicolantonio, F. , Giordano, S. , Siena, S. , 2013. Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 3, 658–673. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benvenuti, S. , Sartore-Bianchi, A. , Di Nicolantonio, F. , Zanon, C. , Moroni, M. , Veronese, S. , Siena, S. , Bardelli, A. , 2007. Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res. 67, 2643–2648. - PubMed
-
- Bertotti, A. , Migliardi, G. , Galimi, F. , Sassi, F. , Torti, D. , Isella, C. , Corà, D. , Di Nicolantonio, F. , Buscarino, M. , Petti, C. , Ribero, D. , Russolillo, N. , Muratore, A. , Massucco, P. , Pisacane, A. , Molinaro, L. , Valtorta, E. , Sartore-Bianchi, A. , Risio, M. , Capussotti, L. , Gambacorta, M. , Siena, S. , Medico, E. , Sapino, A. , Marsoni, S. , Comoglio, P.M. , Bardelli, A. , Trusolino, L. , 2011. A molecularly annotated platform of patient-derived xenografts (“xenopatients”) identifies HER2 as an effective therapeutic target in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 1, 508–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

