Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease
- PMID: 24914037
- PMCID: PMC4103421
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005425
Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease
Abstract
Background: Children with heart disease are frequently exposed to imaging examinations that use ionizing radiation. Although radiation exposure is potentially carcinogenic, there are limited data on cumulative exposure and the associated cancer risk. We evaluated the cumulative effective dose of radiation from all radiation examinations to estimate the lifetime attributable risk of cancer in children with heart disease.
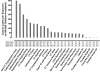
Methods and results: Children ≤6 years of age who had previously undergone 1 of 7 primary surgical procedures for heart disease at a single institution between 2005 and 2010 were eligible for the study. Exposure to radiation-producing examinations was tabulated, and cumulative effective dose was calculated in millisieverts. These data were used to estimate lifetime attributable risk of cancer above baseline using the approach of the Committee on Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation VII. The cohort included 337 children exposed to 13 932 radiation examinations. Conventional radiographs represented 92% of examinations, whereas cardiac catheterization and computed tomography accounted for 81% of cumulative exposure. Overall median cumulative effective dose was 2.7 mSv (range, 0.1-76.9 mSv), and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer was 0.07% (range, 0.001%-6.5%). Median lifetime attributable risk of cancer ranged widely depending on surgical complexity (0.006%-1.6% for the 7 surgical cohorts) and was twice as high in females per unit exposure (0.04% versus 0.02% per 1-mSv effective dose for females versus males, respectively; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Overall radiation exposures in children with heart disease are relatively low; however, select cohorts receive significant exposure. Cancer risk estimation highlights the need to limit radiation dose, particularly for high-exposure modalities.
Keywords: catheterization; imaging; pediatrics; radiography.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
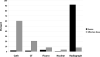
Comment in
-
Reduction of radiation to children: our responsibility to change.Circulation. 2014 Jul 8;130(2):135-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.010699. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Circulation. 2014. PMID: 24914036 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Bardo regarding article, "Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease".Circulation. 2015 Apr 21;131(16):e416. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.012646. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25901075 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Glatz et al regarding article, "Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease".Circulation. 2015 Apr 21;131(16):e417. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.012944. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25901076 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Harbron regarding article, "Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease".Circulation. 2015 Apr 21;131(16):e418. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013009. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25901077 No abstract available.
-
Response to letters regarding article, "Cumulative radiation exposure and cancer risk estimation in children with heart disease".Circulation. 2015 Apr 21;131(16):e419-20. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013266. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 25901078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andreassi MG. Radiation risk from pediatric cardiac catheterization: friendly fire on children with congenital heart disease. Circulation. 2009;120:1847–1849. - PubMed
-
- Beels L, Bacher K, De Wolf D, Werbrouck J, Thierens H. γ-H2AX foci as a biomarker for patient x-ray exposure in pediatric cardiac catheterization: are we underestimating radiation risk? Circulation. 2009;120:1903–1909. - PubMed
-
- Bacher K, Bogaert E, Lapere R, De Wolf D, Thierens H. Patient-specific dose and radiation risk estimation in pediatric cardiac catheterization. Circulation. 2005;111:83–89. - PubMed
-
- El Sayed MH, Roushdy AM, El Farghaly H, El Sherbini A. Radiation exposure in children during the current era of pediatric cardiac intervention. Pediatr Cardiol. 2012;33:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Yakoumakis E, Kostopoulou H, Makri T, Dimitriadis A, Georgiou E, Tsalafoutas I. Estimation of radiation dose and risk to children undergoing cardiac catheterization for the treatment of a congenital heart disease using Monte Carlo simulations. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43:339–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

