'Hit and run' serial femtosecond crystallography of a membrane kinase in the lipid cubic phase
- PMID: 24914170
- PMCID: PMC4052879
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0621
'Hit and run' serial femtosecond crystallography of a membrane kinase in the lipid cubic phase
Abstract
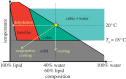
The lipid-based bicontinuous cubic mesophase is a nanoporous membrane mimetic with applications in areas that include medicine, personal care products, foods and the basic sciences. An application of particular note concerns it use as a medium in which to grow crystals of membrane proteins for structure determination by X-ray crystallography. At least two variations of the mesophase exist. One is the highly viscous cubic phase, which has well developed long-range order. The other so-called sponge phase is considerably more fluid and lacks long-range order. The sponge phase has recently been shown to be a convenient vehicle for delivering microcrystals of membrane proteins to an X-ray free-electron laser beam for serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX). Unfortunately, the sponge phase approach calls for large amounts of protein that are not always available in the case of membrane proteins. The cubic phase offers the advantage of requiring significantly less protein for SFX but comes with its own challenges. Here, we describe the physico-chemical bases for these challenges, solutions to them and prospects for future uses of lipidic mesophases in the SFX arena.
Keywords: X-ray free-electron laser; crystal structure; enzyme; membrane protein; mesophase; monoacylglycerol.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Femtosecond crystallography of membrane proteins in the lipidic cubic phase.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;369(1647):20130314. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0314. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24914147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of microcrystals in lipidic cubic phase for serial femtosecond crystallography.Nat Protoc. 2014 Sep;9(9):2123-34. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.141. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Nat Protoc. 2014. PMID: 25122522 Free PMC article.
-
Microcrystallization techniques for serial femtosecond crystallography using photosystem II from Thermosynechococcus elongatus as a model system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;369(1647):20130316. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0316. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24914149 Free PMC article.
-
Serial Femtosecond Crystallography of Membrane Proteins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;922:151-160. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-35072-1_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27553241 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid sample delivery techniques for serial femtosecond crystallography.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;369(1647):20130337. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0337. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24914163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipidic cubic phase injector is a viable crystal delivery system for time-resolved serial crystallography.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 22;7:12314. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12314. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27545823 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidic cubic phase serial millisecond crystallography using synchrotron radiation.IUCrJ. 2015 Jan 27;2(Pt 2):168-76. doi: 10.1107/S2052252514026487. eCollection 2015 Mar 1. IUCrJ. 2015. PMID: 25866654 Free PMC article.
-
Serial femtosecond crystallography opens new avenues for Structural Biology.Protein Pept Lett. 2016;23(3):255-72. doi: 10.2174/0929866523666160120152937. Protein Pept Lett. 2016. PMID: 26786767 Free PMC article.
-
In meso in situ serial X-ray crystallography of soluble and membrane proteins at cryogenic temperatures.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016 Jan;72(Pt 1):93-112. doi: 10.1107/S2059798315021683. Epub 2016 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 26894538 Free PMC article.
-
Acoustic Injectors for Drop-On-Demand Serial Femtosecond Crystallography.Structure. 2016 Apr 5;24(4):631-640. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.02.007. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Structure. 2016. PMID: 26996959 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

