Complement fixing polysaccharides from Terminalia macroptera root bark, stem bark and leaves
- PMID: 24914893
- PMCID: PMC6270672
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19067440
Complement fixing polysaccharides from Terminalia macroptera root bark, stem bark and leaves
Abstract
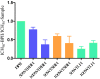
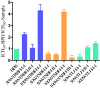
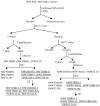
The root bark, stem bark and leaves of Terminalia macroptera were sequentially extracted with ethanol, 50% ethanol-water, and 50 °C and 100 °C water using an accelerated solvent extractor. Ten bioactive purified polysaccharide fractions were obtained from those crude extracts after anion exchange chromatography and gel filtration. The polysaccharides and their native extracts were characterized with respect to molecular weight, chemical compositions and effects in the complement assay. The chemical compositions showed that the polysaccharides are of pectic nature. The results indicated that there was no great difference of the complement fixation activities in the crude extracts from the different plant parts when extracting with the accelerated solvent extraction system. The purified polysaccharide fractions 100WTSBH-I-I and 100WTRBH-I-I isolated from the 100 °C water extracts of stem and root bark respectively, showed the highest complement fixation activities. These two fractions have rhamnogalacturonan type I backbone, but only 100WTSBH-I-I contains side chains of both arabinogalactan type I and II. Based on the yield and activities of the fractions studied those from the root bark gave highest results, followed by those from leaves and stem bark. But in total, all plant materials are good sources for fractions containing bioactive polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomodulating pectins from root bark, stem bark, and leaves of the Malian medicinal tree Terminalia macroptera, structure activity relations.Carbohydr Res. 2015 Feb 11;403:167-73. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 21. Carbohydr Res. 2015. PMID: 24909378
-
Complement activity of polysaccharides from three different plant parts of Terminalia macroptera extracted as healers do.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):672-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.017. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24933222
-
Enzyme inhibition, antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities, and brine shrimp toxicity of extracts from the root bark, stem bark and leaves of Terminalia macroptera.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25017373
-
Polysaccharides with immunomodulating properties from the bark of Parkia biglobosa.Carbohydr Polym. 2014 Jan 30;101:457-63. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.082. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Carbohydr Polym. 2014. PMID: 24299798
-
A Survey of Plant Iron Content-A Semi-Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2015 Dec 10;7(12):10320-51. doi: 10.3390/nu7125535. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26690470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and Biocompatibility Properties In Vitro of Gel Beads Based on the Pectin and κ-Carrageenan.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jan 22;20(2):94. doi: 10.3390/md20020094. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35200624 Free PMC article.
-
New Inonotus Polysaccharides: Characterization and Anticomplementary Activity of Inonotus rheades Mycelium Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;15(5):1257. doi: 10.3390/polym15051257. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904498 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, characterisation and complement fixation activity of acidic polysaccharides from Argemone mexicana used as antimalarials in Mali.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1278-1285. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2089691. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35797701 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnopharmacology, Chemistry and Biological Properties of Four Malian Medicinal Plants.Plants (Basel). 2017 Feb 21;6(1):11. doi: 10.3390/plants6010011. Plants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28230801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Silva O., Gomes E.T., Wolfender J.L., Marston A., Hostettmann K. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with ultraviolet spectroscopy and electrospray mass spectrometry to the characterisation of ellagitannins from Terminalia macroptera roots. Pharmaceut. Res. 2000;17:1396–1401. doi: 10.1023/A:1007598922712. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

