Qualitative and quantitative analysis of triterpene saponins from tea seed pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and their activities against bacteria and fungi
- PMID: 24914901
- PMCID: PMC6271494
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19067568
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of triterpene saponins from tea seed pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel) and their activities against bacteria and fungi
Abstract
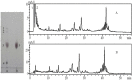
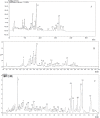
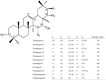
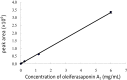
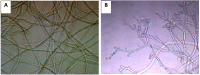
A method using LC-ESI-IT-TOF/MS and LC/UV-ELSD was established to qualitatively analyze triterpene saponins obtained from the tea seed pomace (Camellia oleifera Abel). In addition, the quantitative analysis of oleiferasaponin A1 using LC/UV was developed. The purified total saponins did not exhibit any inhibitory effects at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 mg/mL against the tested bacteria, except for Staphyloccocus aureus and Escherichia coli. By contrast, higher inhibitory activity was seen against the tested fungi, especially against Bipolaris maydis. Following treatment with an MIC value of 250 μg/mL for 24 h, the mycelial morphology was markedly shriveled in appearance or showed flattened and empty hyphae, with fractured cell walls, ruptured plasmalemma and cytoplasmic coagulation or leakage. These structural changes hindered the growth of mycelia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Huang H.Q., Zhang X., Xu Z.X., Su J., Yan S.K., Zhang W.D. Fast determination of saikosaponins in Bupleurum by rapid resolution liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2009;49:1048–1055. - PubMed
-
- Hu J.L., Nie S.P., Huang D.F., Li C., Xie M.Y. Extraction of saponin from Camellia oleifera cake and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012;47:1676–1687.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

