A point mutation in the [2Fe-2S] cluster binding region of the NAF-1 protein (H114C) dramatically hinders the cluster donor properties
- PMID: 24914968
- PMCID: PMC4051502
- DOI: 10.1107/S1399004714005458
A point mutation in the [2Fe-2S] cluster binding region of the NAF-1 protein (H114C) dramatically hinders the cluster donor properties
Abstract
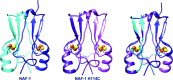
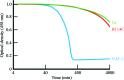
NAF-1 is an important [2Fe-2S] NEET protein associated with human health and disease. A mis-splicing mutation in NAF-1 results in Wolfram Syndrome type 2, a lethal childhood disease. Upregulation of NAF-1 is found in epithelial breast cancer cells, and suppression of NAF-1 expression by knockdown significantly suppresses tumor growth. Key to NAF-1 function is the NEET fold with its [2Fe-2S] cluster. In this work, the high-resolution structure of native NAF-1 was determined to 1.65 Å resolution (R factor = 13.5%) together with that of a mutant in which the single His ligand of its [2Fe-2S] cluster, His114, was replaced by Cys. The NAF-1 H114C mutant structure was determined to 1.58 Å resolution (R factor = 16.0%). All structural differences were localized to the cluster binding site. Compared with native NAF-1, the [2Fe-2S] clusters of the H114C mutant were found to (i) be 25-fold more stable, (ii) have a redox potential that is 300 mV more negative and (iii) have their cluster donation/transfer function abolished. Because no global structural differences were found between the mutant and the native (wild-type) NAF-1 proteins, yet significant functional differences exist between them, the NAF-1 H114C mutant is an excellent tool to decipher the underlying biological importance of the [2Fe-2S] cluster of NAF-1 in vivo.
Keywords: 2Fe–2S cluster transfer and cluster stability; WFS2; autophagy; breast cancer; longevity; redox potential.
Figures
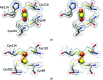


References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
-
- Boucquey, M., De Plaen, E., Locker, M., Poliard, A., Mouillet-Richard, S., Boon, T. & Kellermann, O. (2006). J. Neurochem. 99, 657–669. - PubMed
-
- Chang, N. C., Nguyen, M., Bourdon, J., Risse, P.-A., Martin, J., Danialou, G., Rizzuto, R., Petrof, B. J. & Shore, G. C. (2012). Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 2277–2287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

