Influence of elastin-like polypeptide and hydrophobin on recombinant hemagglutinin accumulations in transgenic tobacco plants
- PMID: 24914995
- PMCID: PMC4051685
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099347
Influence of elastin-like polypeptide and hydrophobin on recombinant hemagglutinin accumulations in transgenic tobacco plants
Abstract
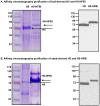
Fusion protein strategies are useful tools to enhance expression and to support the development of purification technologies. The capacity of fusion protein strategies to enhance expression was explored in tobacco leaves and seeds. C-terminal fusion of elastin-like polypeptides (ELP) to influenza hemagglutinin under the control of either the constitutive CaMV 35S or the seed-specific USP promoter resulted in increased accumulation in both leaves and seeds compared to the unfused hemagglutinin. The addition of a hydrophobin to the C-terminal end of hemagglutinin did not significantly increase the expression level. We show here that, depending on the target protein, both hydrophobin fusion and ELPylation combined with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) targeting induced protein bodies in leaves as well as in seeds. The N-glycosylation pattern indicated that KDEL sequence-mediated retention of leaf-derived hemagglutinins and hemagglutinin-hydrophobin fusions were not completely retained in the ER. In contrast, hemagglutinin-ELP from leaves contained only the oligomannose form, suggesting complete ER retention. In seeds, ER retention seems to be nearly complete for all three constructs. An easy and scalable purification method for ELPylated proteins using membrane-based inverse transition cycling could be applied to both leaf- and seed-expressed hemagglutinins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein body formation in stable transgenic tobacco expressing elastin-like polypeptide and hydrophobin fusion proteins.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 May 10;13:40. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-40. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23663656 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-based inverse transition cycling: an improved means for purifying plant-derived recombinant protein-elastin-like polypeptide fusions.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(5):2808-21. doi: 10.3390/ijms12052808. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21686152 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of elastin-like peptide fusions on the quantity and quality of a tobacco-derived human immunodeficiency virus-neutralizing antibody.Plant Biotechnol J. 2009 Dec;7(9):899-913. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009.00452.x. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Plant Biotechnol J. 2009. PMID: 19843249
-
Biotechnological applications of elastin-like polypeptides and the inverse transition cycle in the pharmaceutical industry.Protein Expr Purif. 2019 Jan;153:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Protein Expr Purif. 2019. PMID: 30217600 Review.
-
Elastin-like polypeptides revolutionize recombinant protein expression and their biomedical application.Trends Biotechnol. 2010 Jan;28(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Trends Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 19897265 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Expression of Zika NS2B Protein Antigen in Nicotiana benthamiana and Use for Arboviruses Diagnosis.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 8;10(2):2184-2196. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08998. eCollection 2025 Jan 21. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39866622 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Protein Quantity and Quality-The Next Level of Plant Molecular Farming.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1326. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031326. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-based solutions for veterinary immunotherapeutics and prophylactics.Vet Res. 2014 Dec 31;45(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0117-4. Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25559098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Hydrophobin Fusion Tags for Plant-Produced Fusion Proteins.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 5;11(10):e0164032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164032. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27706254 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro-Formulated Oligomers of Strep-Tagged Avian Influenza Haemagglutinin Produced in Plants Cause Neutralizing Immune Responses.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018 Aug 20;6:115. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00115. eCollection 2018. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30177967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischer R, Schillberg S (2004) Plant-made pharmaceuticals and technical proteins. Weinheim: WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. 315 p.
-
- Floss DM, Rose-John S, Scheller J (2013) ELP fusion technology for biopharmaceuticals. In: Schmidt SR, editor. Fusion protein technologies for biopharmaceuticals: applications and challenges. Hoboken, New Jersey, USA.: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.pp. 211–226.
-
- Stoger E, Ma J, Fischer R, Christou P (2005) Sowing the seeds of success: pharmaceutical proteins from plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16: 167–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

