Anticancer properties of peptide fragments of hair proteins
- PMID: 24915193
- PMCID: PMC4051607
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098073
Anticancer properties of peptide fragments of hair proteins
Abstract
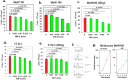
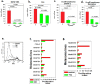
The primary function of hair and fur covering mammalian skin is to provide mechanical and thermal protection for the body. The proteins that constitute hair are extremely resistant to degradation by environmental factors. However, even durable materials can be slowly broken down by mechanical stresses, biodegradation mediated by endogenous enzymes in the skin or host microbes. We hypothesised that the biodegradation products of hair may possess bioprotective properties, which supplement their physical protective properties. Although evolutionary processes have led to a reduction in the amount of hair on the human body, it is possible that the bioprotective properties of hair biodegradation products have persisted. The human skin is exposed to various environmental carcinogenic factors. Therefore, we hypothesised that the potential bioprotective mechanisms of hair degradation products affect melanoma growth. We used pepsin to partially digest hair enzymatically, and this process produced a water-soluble lysate containing a mixture of peptides, including fragments of keratin and keratin-associated proteins. We found out that the mixtures of soluble peptides obtained from human hair inhibited the proliferation of human melanoma cells in vitro. Moreover, the hair-derived peptide mixtures also inhibited the proliferation of B lymphoma cells and urinary bladder cancer cells. Normal human cells varied in their susceptibility to the effects of the lysate; the hair-derived peptide mixtures modulated the proliferation of normal human fibroblasts but did not inhibit the proliferation of human mesenchymal cells derived from umbilical cord stromal cells. These results suggest that hair-derived peptides may represent a new class of anti-proliferative factors derived from basically structural proteins. Identification of active regulatory compounds and recognition of the mechanism of their action might pave the way to elaboration of new anticancer drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rogers MA, Langbein L, Winter H, Ehmann C, Praetzel S, et al. (2001) Characterization of a Cluster of Human High/Ultrahigh Sulfur Keratin-associated Protein Genes Embedded in the Type I Keratin Gene Domain on Chromosome 17q12-21. J Biol Chem 276: 19440–19451. - PubMed
-
- Rogers M A, Winter H, Langbein L, Wolf C, Schweizer J (2000) Characterization of a 300 kbp region of human DNA containing the type II hair keratin gene domain. J Invest Dermatol 114: 464–472. - PubMed
-
- Rogers M A, Winter H, Wolf C, Heck M, Schweizer J (1998) Characterization of a 190-Kilobase Pair Domain of Human Type I Hair Keratin Genes. J Biol Chem 273: 26683–26691. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs E, Weber K (1994) Intermediate filaments: structure, dynamics, function, and disease. Annu Rev Biochem 63: 345–382. - PubMed
-
- Steinert PM, Steven AC, Roop DR (1985) The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell 42: 411–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

