Association of a low-frequency variant in HNF1A with type 2 diabetes in a Latino population
- PMID: 24915262
- PMCID: PMC4425850
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2014.6511
Association of a low-frequency variant in HNF1A with type 2 diabetes in a Latino population
Erratum in
- JAMA. 2014 Nov 12:312(18):1932. Jiménez-Morales, Silvia[Added]
Abstract
Importance: Latino populations have one of the highest prevalences of type 2 diabetes worldwide.
Objectives: To investigate the association between rare protein-coding genetic variants and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in a large Latino population and to explore potential molecular and physiological mechanisms for the observed relationships.
Design, setting, and participants: Whole-exome sequencing was performed on DNA samples from 3756 Mexican and US Latino individuals (1794 with type 2 diabetes and 1962 without diabetes) recruited from 1993 to 2013. One variant was further tested for allele frequency and association with type 2 diabetes in large multiethnic data sets of 14,276 participants and characterized in experimental assays.
Main outcome and measures: Prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Secondary outcomes included age of onset, body mass index, and effect on protein function.
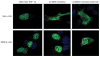
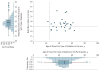
Results: A single rare missense variant (c.1522G>A [p.E508K]) was associated with type 2 diabetes prevalence (odds ratio [OR], 5.48; 95% CI, 2.83-10.61; P = 4.4 × 10(-7)) in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-α (HNF1A), the gene responsible for maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 (MODY3). This variant was observed in 0.36% of participants without type 2 diabetes and 2.1% of participants with it. In multiethnic replication data sets, the p.E508K variant was seen only in Latino patients (n = 1443 with type 2 diabetes and 1673 without it) and was associated with type 2 diabetes (OR, 4.16; 95% CI, 1.75-9.92; P = .0013). In experimental assays, HNF-1A protein encoding the p.E508K mutant demonstrated reduced transactivation activity of its target promoter compared with a wild-type protein. In our data, carriers and noncarriers of the p.E508K mutation with type 2 diabetes had no significant differences in compared clinical characteristics, including age at onset. The mean (SD) age for carriers was 45.3 years (11.2) vs 47.5 years (11.5) for noncarriers (P = .49) and the mean (SD) BMI for carriers was 28.2 (5.5) vs 29.3 (5.3) for noncarriers (P = .19).
Conclusions and relevance: Using whole-exome sequencing, we identified a single low-frequency variant in the MODY3-causing gene HNF1A that is associated with type 2 diabetes in Latino populations and may affect protein function. This finding may have implications for screening and therapeutic modification in this population, but additional studies are required.
Figures

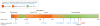

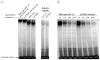
References
-
- Villalpando S, de la Cruz V, Rojas R, et al. Prevalence and distribution of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Mexican adult population. Salud Publica Mex. 2010;52(suppl 1):S19–S26. - PubMed
-
- Barquera S, Tovar-Guzmán V, Campos-Nonato I, González-Villalpando C, Rivera-Dommarco J. Geography of diabetes mellitus mortality in Mexico. Arch Med Res. 2003;34(5):407–414. - PubMed
-
- Cowie CC, Rust KF, Byrd-Holt DD, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in adults in the U.S. population: National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(6):1263–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA80205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057295/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA144034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL045522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35CA53890/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK053889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057295/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK042273/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA053890/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL045522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK047482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL24799/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

