Flupenthixol decanoate (depot) for schizophrenia or other similar psychotic disorders
- PMID: 24915451
- PMCID: PMC7057031
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001470.pub2
Flupenthixol decanoate (depot) for schizophrenia or other similar psychotic disorders
Abstract
Background: Long-acting depot injections of drugs such as flupenthixol decanoate are extensively used as a means of long-term maintenance treatment for schizophrenia.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of flupenthixol decanoate in comparison with placebo, oral antipsychotics and other depot neuroleptic preparations for people with schizophrenia and other severe mental illnesses, in terms of clinical, social and economic outcomes.
Search methods: We identified relevant trials by searching the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register in March 2009 and then for this update version, a search was run in April 2013. The register is based on regular searches of CINAHL, EMBASE, MEDLINE and PsycINFO. References of all identified studies were inspected for further trials. We contacted relevant pharmaceutical companies, drug approval agencies and authors of trials for additional information.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials that focused on people with schizophrenia or other similar psychotic disorders where flupenthixol decanoate had been compared with placebo or other antipsychotic drugs were included. All clinically relevant outcomes were sought.
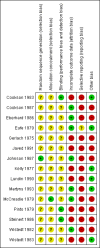
Data collection and analysis: Review authors independently selected studies, assessed trial quality and extracted data. For dichotomous data we estimated risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a fixed-effect model. Analysis was by intention-to-treat. We summated normal continuous data using mean difference (MD), and 95% CIs using a fixed-effect model. We presented scale data only for those tools that had attained prespecified levels of quality. Using Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) we created 'Summary of findings tables and assessed risk of bias for included studies.
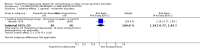
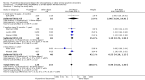
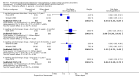
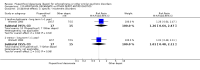
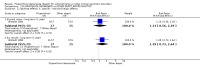
Main results: The review currently includes 15 randomised controlled trials with 626 participants. No trials compared flupenthixol decanoate with placebo.One small study compared flupenthixol decanoate with an oral antipsychotic (penfluridol). Only two outcomes were reported with this single study, and it demonstrated no clear differences between the two preparations as regards leaving the study early (n = 60, 1 RCT, RR 3.00, CI 0.33 to 27.23,very low quality evidence) and requiring anticholinergic medication (1 RCT, n = 60, RR 1.19, CI 0.77 to 1.83, very low quality evidence).Ten studies in total compared flupenthixol decanoate with other depot preparations, though not all studies reported on all outcomes of interest. There were no significant differences between depots for outcomes such as relapse at medium term (n = 221, 5 RCTs, RR 1.30, CI 0.87 to 1.93, low quality evidence), and no clinical improvement at short term (n = 36, 1 RCT, RR 0.67, CI 0.36 to 1.23, low quality evidence). There was no difference in numbers of participants leaving the study early at short/medium term (n = 161, 4 RCTs, RR 1.23, CI 0.76 to 1.99, low quality evidence) nor with numbers of people requiring anticholinergic medication at short/medium term (n = 102, 3 RCTs, RR 1.38, CI 0.75 to 2.25, low quality evidence).Three studies in total compared high doses (100 to 200 mg) of flupenthixol decanoate with the standard doses (˜40mg) per injection. Two trials found relapse at medium term (n = 18, 1 RCT, RR 1.00, CI 0.27 to 3.69, low quality evidence) to be similar between the groups. However people receiving a high dose had slightly more favourable medium term mental state results on the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) (n = 18, 1 RCT, MD -10.44, CI -18.70 to -2.18, low quality evidence). There was also no significant difference in the use of anticholinergic medications to deal with side effects at short term (2 RCTs n = 47, RR 1.12, CI 0.83 to 1.52 very low quality evidence). One trial comparing a very low dose of flupenthixol decanoate (˜6 mg) with a low dose (˜9 mg) per injection reported no difference in relapse rates (n = 59, 1 RCT, RR 0.34, CI 0.10 to 1.15, low quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: In the current state of evidence, there is nothing to choose between flupenthixol decanoate and other depot antipsychotics. From the data reported in clinical trials, it would be understandable to offer standard dose rather than the high dose depot flupenthixol as there is no difference in relapse. However, data reported are of low or very low quality and this review highlights the need for large, well-designed and reported randomised clinical trials to address the effects of flupenthixol decanoate.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures













Update of
-
Depot flupenthixol decanoate for schizophrenia or other similar psychotic disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001470. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001470. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 10;(6):CD001470. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001470.pub2. PMID: 10796442 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cookson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Cookson IB, Muthu MS, George A, Dewey M. High dose neuroleptic treatment of chronic schizophrenic inpatients. Research Communications in Psychology, Psychiatry and Behaviour 1983;8(4):305‐15.
Cookson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cookson IB. The effects of a 50% reduction of cis(Z)‐flupenthixol decanoate in chronic schizophrenic patients maintained on a high dose regime. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1987;2:141‐9. - PubMed
Eberhard 1986 {published data only}
-
- Eberhard G. Depot antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients: a comparison between haloperidol decanoate and flupenthixol decanoate. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1986;Suppl 1:27.
-
- Eberhard G, Hellbom E. Haloperidol decanoate and flupenthixol decanoate in schizophrenia. A long‐term double‐blind cross‐over comparison. Acta Psychiatria Scandinavica 1986;74:255‐62. - PubMed
Eufe 1979 {published data only}
-
- Eufe R, Wegener G. Double‐blind comparison of 2 depot neuroleptics (perphenazine enanthate and flupentixol decanoate) in chronic schizophrenia (author's transl) [Doppelblindvergleich von 2 depotneuroleptika (Perphenazin‐onanthat und flupentixol‐decaoat bei chronischer schizophrenie)]. Nervenarzt 1979;50:534‐9. - PubMed
Gerlach 1975 {published data only}
-
- Gerlach J, Kramp P, Kristjansen P, Lauritsen B, Luhdorf K, Munkvad I. Peroral and parenteral administration of long‐acting neuroleptics: a double‐blind study of penfluridol compared to flupenthixol decanoate in the treatment of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1975;52:132‐44. - PubMed
Javed 1991 {published data only}
-
- Javed MA, Chaudhry MR. Double blind comparison of flupenthixol decanoate and fluphenazine decanoate in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Pakistan Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1991;1(2):69‐74.
Johnson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Johnson DAW, Ludlow JM, Street K, Taylor RDW. Double‐blind comparison of half‐dose and standard‐dose flupenthixol decanoate in the maintenance treatment of stabilised out‐patients with schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;151:634‐8. - PubMed
Kelly 1977 {published data only}
-
- Kelly HB, Freeman HL, Banning B, Schiff AA. Clinical and social comparison of fluphenazine decanoate and flupenthixol decanoate in the community maintenance therapy of schizophrenia. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1977;12:54‐64. - PubMed
Lundin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lundin L, Dencker SJ, Malm U. Community‐based rehabilitation of schizophrenia. Nordisk Psykiatrisk Tidsskrift 1990;44:81‐7.
Martyns 1993 {published data only}
-
- Martyns‐Yellowe IS. The decanoates of flupenthixol and clopenthixol in the treatment of chronic schizophrenic in‐patients implications for community psychiatry. West African Journal of Medicine 1993;12(2):110‐2. - PubMed
McCreadie 1979 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie RG, Flanagan WL, McKnight J, Jorgensen A. High dose flupenthixol decanoate in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;135:175‐9. - PubMed
Pinto 1979 {published data only}
-
- Pinto R, Banerjee A, Ghosh N. A double‐blind comparison of flupenthixol decanoate and fluphenazine decanoate in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1979;60:313‐22. - PubMed
Steinert 1986 {published data only}
-
- Steinert J, Erba E, Pugh CR, Robinson C, Preist RG. A comparative trial of depot pipothiazine. Journal of International Medical Research 1986;14:72‐7. - PubMed
Wistedt 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wistedt B, Jorgensen A, Wiles D. A depot withdrawal study. Palsma concentration of fluphenazine and flupenthixol and relapse frequency. Psychopharmacology 1982;78:301‐4. - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B, Wiles D, Jorgensen A. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study neurological effects. Psychopharmacology 1983;80:101‐5. - PubMed
Wistedt 1983 {published data only}
-
- Wistedt B, Ranta J. Comparative double‐blind study of flupenthixol decanoate and fluphenazine decanoate in the treatment of patients relapsing in a schizophrenic symptomatology. Acta Psychiatria Scandanavica 1983;67:378‐88. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Arango 1999 {published data only}
-
- Arango C. Oral or depot antipsychotics for people with schizophrenia and a history of violence. Stanley Foundation Research Programs 1999.
Astrup 1974 {published data only}
-
- Astrup C, Grimsgard A, Hebnes K, Kruse‐Jensen A, Lid M. A study of flupenthixol decanoate and pipothiazine undecylenate in schizophrenics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1974;50:481‐91. - PubMed
Bakke 1973 {published data only}
-
- Bakke O. Clinical experience with DEPOT neuroleptics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1973;246:32‐41. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Barnes 1983 {published data only}
-
- Barnes TR, Milavic G, Curson DA, Platt SD. Use of the Social Behaviour Assessment Schedule (SBAS) in a trial of maintenance antipsychotic therapy in schizophrenic. Social Psychiatry 1983;18(4):193‐9. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Benkert 1996 {published data only}
-
- Benkert O, Müller‐Siecheneder F, Wetzel H. Negative and depressive symptoms in acute schizophrenic episodes‐ do they improve under neuroleptic treatment?. 8th Congress of the Association of European Psychiatrists; 1996 Jul 7‐12; London, UK. 1996. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ]
Bombin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bombin I, Arango C. Antipsychotic treatment adherence and violence in schizophrenia outpatients: a randomized prospective trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2004;14(Suppl.3):S289.
Burns 2001a {published data only}
-
- Burns T, Bale R. Clinical advantages of amisulpride in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Journal of International Medical Research 2001;29(6):451‐66. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PSYCINFO] - PubMed
Chanpattana 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chanpattana W. ECT in Schizophrenia. Journal of the Psychiatric Association of Thailand 1999;44(2):156‐70. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ]
-
- Chanpattana W, Chakrabhand ML, Kirdcharoen N, Tuntirungsee Y, Techakasem P, Prasertsuk Y. The use of the stabilization period in electroconvulsive therapy research in schizophrenia: II. Implementation. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1999;82(6):558‐68. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chanpattana W, Chakrabhand ML, Kirdcharoen N, Tuntirungsee Y, Techakasem P, Prasertsuk Y. The use of the stabilization period in electroconvulsive therapy research in schizophrenia: II. Implementation. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1999;82(6):558‐68. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chanpattana W, Chakrabhand ML, Sackeim HA, Kitaroonchai W, Kongsakon R, Techakasem P, et al. Continuation ECT in treatment resistant schizophrenia: a controlled study. Journal of ECT 1999;15(3):178‐92. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chanpattana W, Sackeim HA, Techakasem P, Chakrabhand S. ECT in schizophrenia. 152nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1999 May 15‐20; Washington DC, USA. 1999. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ]
Chouinard 1978 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G, Annable L, Kropsky M. A double‐blind controlled study of pipothiazine palmitate in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenic outpatients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1978;18(2‐3):148‐54. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO] - PubMed
Chowdhury 1980 {published data only}
-
- Chowdhury MEH, Chacon C. Depot fluphenazine and flupenthixol in the treatment of stabilized schizophrenics. A double‐blind comparative trial. Comprehensive Psychiatry 1980;21(2):135‐9. - PubMed
Classen 1988 {published data only}
-
- Classen W, Laux G. Sensorimotor and cognitive performance of schizophrenic inpatients treated with haloperidol, flupenthixol, or clozapine. Pharmacopsychiatry 1988;21(6):295‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Colonna 2000 {published data only}
-
- Colonna L, Saleem P, Dondey Nouvel L, Rein W, Bartholome F, Boxus A, et al. Long term safety and efficacy of amisulpride in subchronic or chronic schizophrenia. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2000;15(1):13‐22. [EMBASE: 2000039766; MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cookson 1991 {published data only}
-
- Cookson JC. Side effects during long‐term treatment with depot antipsychotic medication. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1991;14(Suppl 2):S24‐32. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cotes 1977 {published data only}
-
- Cotes PM, Crow TJ, Johnstone EC. Serum prolactin as an index of dopamine receptor blockade in acute schizophrenia. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1977;4:651P. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coufal 1981 {published data only}
-
- Coufal J, Novotny M. Fluphenazine and flupenthixol decanoate in psychiatric outpatients practice. Activa Nervosa Superior (Praha) 1981;23(4):269‐71. - PubMed
Crow 1977 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, Frith C, Johnstone EC. The clinical effects of the isomers of flupenthixol: the consequences of dopamine receptor blockade in acute schizophrenia (Proceedings). British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1977;4(5):648P. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Crow 1986 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148(2):120‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PASCAL] - PubMed
Curson 1985 {published data only}
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long‐term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out patients: the seven year follow‐up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. II. The incidence of compliance problems, side‐effects, neurotic symptoms and depression. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:469‐74. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long‐term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out‐patients: the seven year follow‐up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine‐ placebo trial I. Course of illness, stability of diagnosis, and the role of a special maintenance clinic. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:464‐9. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long‐term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out‐patients: the seven year follow‐up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. III. Relapse postponement or relapse prevention? The implications for long‐term outcome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:474‐80. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TRE, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out‐patients: the seven‐year follow‐up of the Medical Reseach Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:464‐80. - PubMed
Dahmen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dahmen N, Muller MJ, Germeyer S, Rujescu D, Anghelescu I, Hiemke C, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of the dopamine D2 and D3 receptor and neuroleptic drug effects in schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Research 2001;49:223‐5. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davies 2007 {published data only}
-
- Davies LM, Lewis S, Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Gaughran F, Hayhurst K, et al. CUTLASS team. Cost‐effectiveness of first‐ v second‐generation antipsychotic drugs: results from a randomised controlled trial in schizophrenia responding poorly to previous therapy. British Journal of Psychiatry 2007;191(July):14‐22. [EMBASE: 2007328135; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Deberdt 1980 {published data only}
-
- Deberdt R, Elens P, Berghmans W, Heykants J, Woestnborghs R, Dreisens F, et al. Clopenthixol and flupenthixol depot preparations in outpatient schizophrenics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1980;62:356‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Demerdash 1981 {published data only}
-
- Demerdash A, Mazhar N, El‐Hanbali M, Abou‐Ghazala E. A double‐blind trial of fluspirilene versus flupenthixol decanoate in the treatment of schizophrenic inpatients. Journal of Kuwait Medical Association 1981;15:7‐16.
Dencker 1980a {published data only}
-
- Dencker SJ, Lepp M, Malm U. Clopenthixol and flupenthixol depot preparations in outpatient schizophrenics. II Factor analysis of the CPRS sub‐scale for schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1980;279:29‐40. [1980262291] - PubMed
-
- Dencker SJ, Lepp M, Malm U. Clopenthixol and flupenthixol depot preparations in outpatient schizophrenics. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1980;4:10‐39. - PubMed
Dencker 1980b {published data only}
-
- Dencker SJ, Lepp M, Malm U. Do schizophrenics well adapted in the community need neuroleptics? A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, Supplementum 1980;279:64‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dittmann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dittmann RW, Geuppert MS, Diehl A, Hubrich P, Maraz, Gattaz WF. Olanzapine versus flupentixol in the treatment of inpatients with schizophrenia: a randomised double‐blind trial. Schizophrenia Research 2001;49(1, 2):225. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO] - PubMed
Dittmann 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dittmann RW, Diehl A, Hubrich P, Maras A, Gattaz WF. Randomized double‐blind trial: olanzapine vs flupenthixol. 12th World Congress of Psychiatry; 2002 Aug 24‐29; Yokohama, Japan. 2002. [EMBASE: 2002386502]
Ehmann 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ehmann TS, Delva NJ, Beninger RJ. Flupenthixol in chronic schizophrenic inpatients: a controlled comparison with haloperidol. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1987;7(3):173‐5. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eli 2001b {published data only}
-
- Eli Lilly, Company. HGBL: olz v flupentixol. Unpublished report 2001.
Faltus 1976 {published data only}
-
- Faltus F, Soucek K. Treatment of schizophrenia using depot neuroleptics [Lecba schizofrenie depotnimi neuroleptiky]. Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 1976;72(3):170‐5. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Floru 1975 {published data only}
-
- Floru L, Heinrich K, Wittek F. The problem of post‐psychotic schizophrenic depressions and pharmacological induction. International Pharmacopsychiatria 1975;10:230‐9. - PubMed
Freeman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Freeman HL. Amisulpride compared with standard neuroleptics in acute exacerbations of schizophrenia: three efficacy studies. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1997;12(Suppl 2):S11‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Frith 1979 {published data only}
-
- Frith CD, Stevens M, Johnstone EC, Crow TJ. Skin conductance responsivity during acute episodes of schizophrenia as a predictor of symptomatic improvement. Psychological Medicine 1979;9(1):101‐6. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gattaz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gattaz WF, Diehl A, Geuppert MS, Hubrich P, Schmitt A, Linde I, et al. Olanzapine versus flupenthixol in the treatment of inpatients with schizophrenia: a randomized double‐blind trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004;37(6):279‐85. [EMBASE: 2004519197; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Genstahler 2001 {published data only}
-
- Genstahler BM. Flupentixol ist Risperidon ebenburtig. Pharmazeutische Zeitung 2001;146(42):30. [BIOSIS: 550227]
Giannelli 1990 {published data only}
-
- Giannelli A, Rabboni M, Zarattini F. Clinical profiles of action, individual treatment preferences, affects and contraindications of three depot neuroleptics compared in a multicentre trial [Profili clinici di azione, indicazioni preferenziali, effetti terapeutici e controindicazioni di tre neurolettici depot in trial multicentrico di confronto]. Rivista di Psichiatria 1990;25(1):7‐24. [PsycINFO]
Glaser 2002 {published data only}
-
- Glaser T, Philipp M, Lesch OM, Walter H, Patras L, Kurtz G, et al. Flupenthixol and risperidone: equivalent efficacy against negative symptoms in schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;5(Suppl 1):S120.
-
- Glaser T, Philipp M, Mast O. Subjective experiences and satisfaction of schizophrenic patients treated with flupenthixol or risperidone: results of a double‐blind trial. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;5(Suppl 1):S120.
Glick 1989 {published data only}
-
- Glick ID, Jacobs M, Lieberman J, Simpson G, Schooler NR. Prediction of short term outcome in schizophrenia: depressive symptoms, negative symptoms, and extrapyramidal signs. Treatment Strategies in Schizophrenia Collaborative Study Group. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989;25(3):344‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Godleski 2000 {published data only}
-
- Godleski LS, Goldsmith LJ, Zettwoch NC, Stikovac DC, Lewis SJ. Depot antipsychotic versus oral olanzapine treatment. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, Illinois, USA. 2000.
Godleski 2003 {published data only}
-
- Godleski LS, Goldsmith LJ, Vieweg WV, Zettwoch NC, Stikovac DM, Lewis SJ. Switching from depot antipsychotic drugs to olanzapine in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2003;64(2):119‐22. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PSYCINFO] - PubMed
Gottfries 1967 {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG. Clinical experiences with flupenthixol in psychiatric patients [Kliniska erfarenheter med flupenthixol pa ett psykosklientel]. Nordisk Psykiatrisk Tidsskrift 1967;21:430‐6. - PubMed
Gottfries 1970a {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG. A double‐blind investigation with flupenthixol and trifluoperazine at treatment of schizophrenic psychoses. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;217:53. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ]
Gottfries 1971 {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG. Flupenthixol and flupenthixol decanoate with special reference to their antipsychotic effect. Acta Psychiatrica Belgica 1974;74(5):507‐16. - PubMed
-
- Gottfries CG. Flupenthixol and trifluoperazine: a double‐blind investigation in the treatment of schizophrenics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1971;119:547‐8. - PubMed
Gottfries 1974 {published data only}
-
- Gottfries CG, Green L. Flupenthixol decanoate in treatment of out‐patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1974;Suppl 255:15‐9. - PubMed
Grunder 1999 {published data only}
-
- Grunder G, Wetzel H, Schlosser R, Anghelescu I, Hillert A, Lange K, et al. Neuroendocrine response to antipsychotics: effects of drug type and gender. Biological Psychiatry 1999;45(1):89‐97. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hamilton 1979 {published data only}
-
- Hamilton M, Card IR, Wallis GG, Mahmoud MR. A comparative trial of the decanoates of flupenthixol and fluphenazine. Psychopharmacology 1979;64:225‐9. - PubMed
Haslam 1975 {published data only}
-
- Haslam MT, Bromham BM, Schiff AA. A comparative trial of fluphenazine decanoate and flupenthixol decanoate. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1975;51:92‐100. - PubMed
Hertling 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hertling I, Dvorak A, Glaser T, Philipp M, Beneke M, Ramskogler K, et al. Influence of psychopathological symptoms on subjective quality of life of schizophrenic patients [Der einfluss psychopathologischer symptome auf die subjektive lebensqualitiat schizophrener patienten]. Psychopharmakotherapie 2003;10(4):151‐8. [EMBASE: 2003494380]
Hillert 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hillert A, Philipp M, Gattaz WF, Sauer H, Adler G, Wetzel H, et al. Amisulpride vs flupentixol in the treatment of schizophrenia with predominant positive symptomatology: a controlled double‐blind study. Neuropyschopharmacology 1994;10(3S):31s. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PSYCINFO]
Hirsch 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch SR, Jolley AG, Manchanda R, McRink A. Intermittent medication as an alternative to maintenance medication in the treatment of schizophrenia: a preliminary report [Fruehzeitige medikamentoese Intervention als Alternative zur Depot‐Dauer‐Medikation in der Schizophreniebehandlung Ein vorlaeufiger Bericht]. In: Boeker W, Brenner HD editor(s). Bewaltigung der Schizophrenie. Bern, Switzerland: Verlag Hans Huber, 1986:62‐71. [PSYNDEX: 20591]
Huang 1995 {published data only}
-
- Huang J, Shuai Y, Cai C. A study on therapeutic efficacy of flupenthixol in treating chronic schizophrenics of type II. Chinese Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 1995;28(5):269‐72. [EMBASE: 1996089743; CAJ]
Ishimaru 1971 {published data only}
-
- Ishimaru T, Kubo S, Ishikawa H, et al. Clinical evaluation on effect of flupentixol, a neuroleptic drug, on schizophrenia by double‐blind controlled trial. Seishin Igaku (Clinical Psychiatry) 1971;13(7):739‐47.
Johnson 1975 {published data only}
-
- Johnson DA, Malik NA. A double‐blind comparison of fluphenazine decanoate and flupenthixol decanoate in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1975;51:257‐67. - PubMed
Johnstone 1978 {published data only}
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow TJ, Frith CD, Carney MW, Price JS. Mechanism of the antipsychotic effect in the treatment of acute schizophrenia. Lancet 1978;1(8069):848‐51. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johnstone 1979 {published data only}
-
- Johnstone EC, Frith CD, Gold A, Stevens M. The outcome of severe acute schizophrenic illnesses after one year. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:28‐33. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jorgensen 1980 {published data only}
-
- Jorgensen A, Overo KF. Clopenthixol and flupenthixol depot preparations in outpatient schizophrenics. III. Serum levels. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1980;61:41‐54. - PubMed
Jorgensen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Jorgensen A, Anderson J, Bjorndal N, Dencker SJ, Lundin L, Malm U. Serum concentrations of cis(Z)‐flupenthixol and prolactin in chronic schizophrenic patients treated with flupenthixol and cis(Z)‐flupenthixol decanoate. Psychopharmacology 1982;77:58‐65. - PubMed
Joseph 1979 {published data only}
-
- Joseph MH, Baker HF, Johnstone EC, Crow TJ. 3‐Methoxy‐4‐hydroxyphenylglycol excretion in acutely schizophrenic patients during a controlled clinical trial of the isomers of flupenthixol. Psychopharmacology 1979;64(1):35‐40. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ju 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ju FY, Wang CZ, Yue XC, Fang YR, Xue HD, Chen SX. Flupentixol vs fluphenazine in schizophrenia patients: a randomized controlled trial. New Drugs and Clinical Remedies 1996;15(1):19‐22.
Kelemen 2006a {published data only}
-
- Kelemen O, Nagy O, Máttyássy A, Kiss I, Janka Z, Kéri S. Do second‐generation antipsychotics disrupt decision‐making abilities in schizophrenia?. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;16(Suppl 4):S430.
King 2002 {published data only}
-
- King KG, Dittmann RW, Diehl A, Hubrich P, Maras A, Gattaz WF. Randomized double‐blind trial: olanzapine vs flupenthixol. 12th World Congress of Psychiatry; 2002 Aug 24‐29; Yokohama, Japan. 2002. [EMBASE: 2002386502]
Kistrup 1991 {published data only}
-
- Kistrup K, Gerlacj J, Aaes‐Jorgensen T, Larsen N. Perphenazine decanoate and cis(z)‐flupenthixol decanoate in maintenance treatment of schizophrenic outpatients. Psychopharmacology 1991;105:42‐8. - PubMed
Knights 1979 {published data only}
-
- Knights A, Okasha MS, Salih MA, Hirsch SR. Depressive and extrapyramidal symptoms and clinical effects: a trial of fluphenazine versus flupenthixol in maintenance of schizophrenic out‐patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;135:515‐23. - PubMed
Kong 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kong DSG, Yeo SH. An open clinical trial with the long‐acting neuroleptics flupenthixol decanoate and fluphenazine decanoate in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Pharmatherapeutica 1989;5:371‐9. - PubMed
Lapierre 1983 {published data only}
-
- Lapierre YD, Frenckell R. AMDP psychopathology factors in chronic schizophrenia: a clinical trial of two long‐acting neuroleptics. Modern Problems of Pharmacopsychiatry 1983;20:193‐203. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Leff 1971 {published data only}
Liu 1999a {published data only}
-
- Liu S. Two year follow up observations on treatments of type schizophrenia with maintenance dose of clozapine or fluanxol. Acta Medicinae Sinica 1999;12(3):266‐7.
Liu 2000a {published data only}
-
- Liu QZ, Wang LH, Han YF, Zhou CL, Wang LH. A comparative study of fluanxol and chlorpromazine used for schizophrenia. Journal of Taishan Medical College 2000;21(2):117‐21.
Macmillan 1984 {published data only}
-
- Macmillan JF. The first schizophrenic illness ‐ presentation and short term outcome, incorporating a trial of prophylactic neuroleptic maintenance therapy versus placebo. PhD dissertation submitted to the University of Edinburgh. Edinburgh, UK: University of Edinburgh, 1984:112‐40. [SIGLE]
MacMillan 1986 {published data only}
-
- MacMillan JF, Crow TJ, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. Short‐term outcome in trial entrants and trial eligible patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148(2):128‐33. [EMBASE: 1986102574; MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PASCAL] - PubMed
McCreadie 1989 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie RG, Wiles D, Grant S, Crockett GT, Mahmood Z, Livingston MG, et al. The Scottish first episode schizophrenia study. VII. Two‐year follow‐up. Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1989;80(6):597‐602. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study V. One‐year follow‐up. The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. British Journal of Psychiatry 1988;152:470‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. II. Treatment: pimozide versus flupenthixol. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:334‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish first episode schizophrenia study. VIII. Five‐year follow‐up: clinical and psychosocial findings. The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. British Journal of Psychiatry 1992;161:496‐500. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- The Scottish Schizophrenia Research Group. The Scottish First Episode Schizophrenia Study. III. Cognitive performance. British Journal of Psychiatry 1987;150:338‐40. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mueller 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mueller MJ BO. Depressive symptoms in acute schizophrenia: evaluation and outcome under new antipsychotics. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1997;7(Suppl 2):S227‐8.
Mueller 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mueller MJ, Wetzel H, Benkert O. Differential effects of high‐dose amisulpride versus flupentixol on latent dimensions of depressive and negative symptomatology in acute schizophrenia: An evaluation using confirmatory factor analysis. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2002;17(5):249‐61. [BIOSIS: 550227] - PubMed
Muller 1997 {published data only}
-
- Muller MJ, Benkert O. Depressive symptoms in acute schizophrenia: evaluation and outcome under new antipsychotics. 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13‐17; Vienna, Austria. 1997. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO]
Muller 1998 {published data only}
-
- Muller MJ, Wetzel H, Benkert O. Differential treatment effects of amisulpride versus flupentixol on latent dimensions of depressive and negative symptoms in acute schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1,2):157. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Müller 1998a {published data only}
-
- Müller MJ, Wetzel H, Benkert O. Depressive symptoms in acute psychotic disorders: evaluation methods and treatment strategies. 21st Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum Congress; 1998 Jul 12‐16; Glasgow, UK. 1998. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ]
-
- Müller MJ, Wetzel H, Benkert O. Latent dimensions of depressive and negative symptoms in acute schizophrenia: treatment effects of high dose amisulpride vs. flupentixol. 11th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1998 Oct 31 ‐ Nov 4; Paris, France. 1998. [11TH: Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology [CD‐ROM]: Conifer, Excerpta Medica Medical Communications BV, 1998]
Owen 1981 {published data only}
-
- Owen F, Bourne RC, Crow TJ, Fadhli AA, Johnstone EC. Platelet monoamine oxidase activity in acute schizophrenia: relationship to symptomatology and neuroleptic medication. British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;139:16‐22. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
O’Regan 2005 {published data only}
-
- O’Regan MK, O’Donnell C, Papas A, Dell’Olio M, Purcell R, McGorry PD. 73% medication compliance needed to achieve therapeutic benefit in first episode psychosis (FEP). Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 2005;39(Suppl 2):A74.
Pach 1998 {published data only}
-
- Pach J, Finkbeiner T, Wolstein J, Glaser T. Maintenance therapy with flupenthixol‐decanoate in chronic schizophrenics: a one‐year follow‐up study. XXIst C.I.N.P. Congress. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998. Awaiting translation.
Parent 1982 {published data only}
-
- Parent M, Toussaint C. Flupenthixol versus haloperidol in acute psychosis. Pharmatherapeutica 1983;3(5):354‐64. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Parent M, Toussaint C. Flupenthixol versus haloperidol in acute psychotic episodes [Flupentixol versus haloperidol dans les episodes psychotiques aigus]. Acta Psychiatrica Belgica 1982;82(6):617‐31. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Philipp 2003 {published data only}
-
- Philipp M, Lesch OM, Schmauss M, Dose M, Glaser T. Comparative effectiveness of flupenthixol and risperidone on negative symptoms [Vergleichbare Wirksamkeit von Flupentixol und Risperidon auf schizophrene Negativsymptomatik]. Psychiatrische Praxis 2003;30(Suppl 2):S94‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reimold 2007 {published data only}
-
- Reimold M, Solbach C, Noda S, Schaefer J‐E, Bartels M, Beneke M, et al. Occupancy of dopamine D(1), D (2) and serotonin (2A) receptors in schizophrenic patients treated with flupentixol in comparison with risperidone and haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 2007;190(2):241‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rein 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rein W, Fleurot O, Turjanski S. Amisulpride improves affective symptoms in acute schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;8(Suppl 2):S231. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PSYCINFO]
-
- Rein W, Turjanski S, Fleurot O. Amisulpride in the treatment of productive schizophrenia. 10th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1996 Aug 23‐28; Madrid, Spain. 1996. [EMBASE: 1995306466]
Ropert 1973 {published data only}
-
- Ropert R, Levy L, Ropert M. Problems posed by trial use of prolonged action neuroleptics in acute psychiatric syndromes [Problemes poses par les essais d'emploi des neuroleptiques a action prolongee (N A P ) dans les syndromes psychiatriques aigus]. Annales Medico‐Psychologiques 1973;1(2):259‐67. [PsycINFO] - PubMed
Ruhrmann 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ruhrmann S, Kissling W, Lesch O‐M, Schmauss M, Seemann U, Philipp M. Efficacy of flupentixol and risperidone in chronic schizophrenia with predominantly negative symptoms. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2007;31(5):1012‐22. [EMBASE: 2007257761; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO] - PubMed
Schlosser 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schlosser R, Grunder G, Anghelescu I, Hillert A, Ewald‐Grunder S, Hiemke C, et al. Long‐term effects of the substituted benzamide derivative amisulpride on baseline and stimulated prolactin levels. Neuropsychobiology 2002;46:33‐40. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PSYCINFO] - PubMed
Simon 1978 {published data only}
-
- Simon P, Fermanian J, Ginestet D, Goujet MA, Peron Magnan P. Standard and long‐acting depot neuroleptics in chronic schizophrenics: an 18‐month open multicentric study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35(7):893‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Singh 1984 {published data only}
-
- Singh AN. Therapeutic efficacy of flupenthixol decanoate in schizoaffective disorder: a clinical evaluation. Journal of International Medical Research 1984;12:17‐22. - PubMed
Stauning 1979 {published data only}
-
- Stauning JA, Kirk L, Jorgensen A. Comparison of serum levels after intramuscular injections of 2% and 10% cis(z)‐flupenthixol decanoate in viscoleo to schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 1979;65(1):69‐72. - PubMed
Steuber 1978 {published data only}
-
- Steuber H, Kind J, Lohrengel S, Muller P. Follow‐up treatment of schizophrenic psychoses: advantages and disadvantages of long‐term medication [Nachbehandlung schizophrener Psychosen: Vor‐ und Nachteile der Langzeitmedikation]. Arzneimittelforschung 1978;28(9):1492‐3. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Strous 2007 {published data only}
-
- Strous RD, Greenbaum L, Kanyas K, Merbl Y, Horowitz A, Karni O, et al. Association of the dopamine receptor interacting protein gene, NEF3, with early response to antipsychotic medication. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2007;10(3):321‐33. [EMBASE: 2007223479] - PubMed
Trueman 1974 {published data only}
-
- Trueman HR, Valentine MG. Flupenthixol decanoate in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1974;124:58‐9. - PubMed
Tuninger 1994 {published data only}
-
- Tuninger E, Axelsson R, Levander S. A 3‐year study of maintenance therapy with depot neuroleptics. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 1994;48(6):409‐17.
Tuninger 1996 {published data only}
-
- Tuninger E, Levander S. Large variations of plasma levels during maintenance treatment with depot neuroleptics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;169:618‐21. - PubMed
Turbott 1985 {published data only}
-
- Turbott J, Villiger J, Hunter L. Neuroleptic serum levels measured by radioreceptor assay in patients receiving intramuscular depot neuroleptics. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:439‐42. - PubMed
Turbott 1987 {published data only}
-
- Turbott J, Villiger J, Hunter L. Depot neuroleptic medication and serum levels by radioreceptor assay: prolactin concentration, electrocardiogram abnormalities and six‐month outcome. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1987;21:327‐38. - PubMed
Vaddadi 1986a {published data only}
-
- Vaddadi KS, Gilleard CJ, Mindham RH, Butler R. A controlled trial of prostaglandin E1 precursor in chronic neuroleptic resistant schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 1986;88(3):362‐7. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vinar 1968 {published data only}
-
- Vinar O, Formankova M, Ruzicka S, Taussigova D. Flupentixol in psychoses. Controlled clinical trial. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1968;10(3):313‐4. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vinar 1976 {published data only}
-
- Vinar O, Taussigova D. Schizophrenic syndromes improving without neuroleptic drug treatment [Schizofrenni syndromy zlepsujici se bez neurolepticke lecby]. Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 1976;72(3):176‐81. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO] - PubMed
Weiden 1993 {published data only}
-
- Weiden P, Schooler NR, Severe JB, Lee JH, Schulz SC. Stabilization and DEPOT neuroleptic dosages. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1993;29(2):269‐75. [EMBASE: 1993311550; MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Weiden 1995a {published data only}
-
- Weiden P, Rapkin B, Zygmunt A, Mort T, Goldman D, Frances A. Postdischarge medication compliance of inpatients converted from an oral to a depot neuroleptic regimen. Psychiatric Services 1995;46(10):1049‐54. [EMBASE: 1995306466] - PubMed
Weisman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Weisman L, Lamberti JS, Price N. A comparison of atypical and DEPOT antipsychotic drugs in preventing jail recidivism among outpatients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2001;49(1,2):278. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO]
Wetzel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wetzel H, Philipp M, Gattaz WF, Sauer H, Adler G, Hillert A, et al. High‐dose amisulpride versus flupentixol in schizophrenia with predominantly positive symptomatology. Pharmacopsychiatry 1995;28:227. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wetzel 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wetzel H, Grunder G, Hillert A, Philipp M, Gattaz WF, Sauer H, et al. Amisulpride versus flupentixol in schizophrenia with predominantly positive symptomatology: a double blind controlled study comparing a selective D2 like antagonist to a mixed D1 /D2 like antagonist. The Amisulpride Study Group. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 1998;137(3):223‐32. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wistedt 1981 {published data only}
-
- Wistedt B. A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. A controlled study of the clinical effects of the withdrawal of depot fluphenazine decanoate and depot flupenthixol decanoate in chronic schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandanavica 1981;64:65‐84. - PubMed
-
- Wistedt B, Palmstierna T. Depressive symptoms in chronic schizophrenic patients after withdrawal of long‐acting neuroleptics. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1983;44:369‐71. - PubMed
Wistedt 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wistedt B. How does the psychiatric patient feel about depot treatment, compulsion or help?. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 1995;Suppl 35:41‐6.
Yin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yin J, Wang H, Li Y. [San fu zuo dun yu lv bing zuo zhi liao jing shen fen lie zheng de guan cha hu li]. Heilongjiang Nursing Journal [Modern Nursing] 2005;11(15):1263‐4. [CAJ]
Youssef 1991a {published data only}
-
- Youssef HA. Duration of neuroleptic treatment and relapse rate: a 5‐year follow‐up study with haloperidol decanoate. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1991;14(Suppl 2):S16‐23. [MEDLINE: ; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Aaes‐Jorgenson 1985
-
- Aaes‐Jorgenson A. Pharmacokinetics of oral and depot neuroleptics ‐ clinical relevance. Symposium Espo. Feb 1, 1985.
Altman 1996
Arnt 1998
-
- Arnt J Skarsfeldt T. Do novel antipsychotics have similar pharmacological characteristics? A review of the evidence. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;18(2):63‐101. - PubMed
Asberg 1978
-
- Asberg M, Montgomery SA, Perris C, Schalling D, Sedvall GA. A comprehensive psychopathological rating scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1978;Suppl 271:5‐27. - PubMed
Bandelow 1998
-
- Bandelow B. Effect of Flupenthixol on Negative symptoms and Depresive syndromes in Schizophrenic patients [Wirkung von Flupentixol auf Negativsymptomatik und depressive Syndrome bei schizophrenen Patienten]. In: Glaser T, Soyka M editor(s). Flupentixol. Typisches oder Atypisches Wirkspektrum?. Darmstadt, Germany: Steinkopff, 1998:66‐77.
Barnes 1994
-
- Barnes TRE, Curson DA. Long term depot antipsychotics. A risk benefit assessment. Drug Safety 1994;10(6):464‐79. - PubMed
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. - PubMed
Carney 1976
-
- Carney MW, Sheffield BF. Comparison of antipsychotic depot injections in the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;129:476‐81. - PubMed
Carpenter 1994
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681‐90. - PubMed
Chouinard 1980
-
- Chouinard G, Ross‐Chouinard A, Annable L. Extrapyramidal symptom rating scale. Canadian Journal of Neurological Science 1980;7:233.
David 1994
-
- David AS, Cutting JC. The Neuropsychology of Schizophrenia. Hove, East Sussex: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1994.
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. In: Abstracts of 8th International Cochrane Colloquium. 2000 Oct 25‐28th; Cape Town, South Africa.
Dencker 1980
-
- Dencker SJ, Lepp M, Malm U. Do schizophrenics well adapted in the community need neuroleptics? A depot neuroleptic withdrawal study. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1980;61(Suppl 279):64‐76. - PubMed
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazer LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7:623‐9. - PubMed
DoH 1996
-
- Department of Health, NHS Executive. Burdens of disease: a discussion document. London: HMSO, 1996.
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. [PubMed: 11914310]. - PubMed
Fielding 1978
-
- Fielding S, Lal H. Behavioural actions of neuroleptics. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH editor(s). Handbook of Psychopharmacology. Vol. 10, New York: Springer, 1978:91‐128.
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59:7‐10. - PubMed
Glaser 1998
-
- Glaser T, Sommermeyer M, Fassbinder M, Mauler F. Receptor binding of flupenthixol and other neuroleptics [Das Rezeptorbindungsprofilvon cis‐Flupentixol. In: Glaser T, Soyka M (eds): Flupentixol. Typisches oderAtypisches Wirkspektrum. Steinkopff; Darmstadt, Germany]. PT06004, XXIst CINP Congress, Glasgow. 1998:6‐21.
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. ECDEU Assessment manual for psychopharmacology. DHEW publication No (ADM). DHEW Publication No. ADM 76–338, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, USA, 1976.. Rockville, MD: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976:124‐585.
Hamilton 1960
Harris 1998
-
- Harris EC, Barraclough B. Excess mortality of mental disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry July 1998;173(7):11‐53. - PubMed
Haynes 1979
-
- Haynes RB, Taylor WD, Sackett DL. Compliance in Health Care. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1979.
Heres 2006
-
- Heres S, Davis J, Maino K, Jetzinger E, Kissling W, Leucht S. Why olanzapine beats risperidone, risperidone beats quetiapine, and quetiapine beats olanzapine. American Journal of Psychiatry 2006;163:185‐94. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org..
Hirsch 1973
Honigfeld 1962
-
- Honigfeld G, Gillis RD, Klett CJ. NOSIE‐30: A treatment sensitive ward behavior scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812. - PubMed
Jablensky 1992
-
- Jablensky A, Sartorius N, Ernberg G, Anker M, Korten A, Cooper JE, et al. Schizophrenia: manifestations, incidence and course indifferent cultures. A World Health Organization ten‐country study. Psychological Medicine Monograph Supplement 1992;20:1‐97. - PubMed
Jorgensen 1971
-
- Jorgensen A, Fredricson Overo K, Hansen V. Metabolism, distribution and excretion of flupenthixol decanoate in dogs and rats. Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica 1971;29(2‐3):339‐59. - PubMed
Jorgensen 1978a
-
- Jorgensen A. A sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay for cis(Z)‐ flupenthixol in human serum. Life Science 1978a;23:1533‐42. - PubMed
Kane 1986
-
- Kane JM, Woerner M, Sarantakos S. Depot neuroleptics: a comparison review of standard, intermediate and low‐dose regimens. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1986;47(Suppl 5):30‐3. - PubMed
Kane 1998
-
- Kane JM, Aguglia E, Carlo Altamura A, Guiterrez JLA, Brunello N, Fleischhacker WW, et al. Guidelines for depot antipsychotic treatment in schizophrenia. European Neuropschopharmacology 1998;8:55‐66. - PubMed
Kato 1969
-
- Kato L, Gozsy B, Roy PB, Trsik T. Antidepressant effects of thioxanthenes. In: Lehmann HE, Ban TA editor(s). The Thioxanthenes, Basel, Karger. Basel: Karger, 1969.
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Knapp 2002
-
- Knapp M, Chisholm D, Leese M, Amaddeo F, Tansella M, Schene A, et al. Comparing patterns and costs of schizophrenia care in five European countries: the EPSILON study. European PsychiatricServices: Inputs Linked to Outcome Domains and Needs. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2002;105(1):42–54. - PubMed
Krawiecka 1977
-
- Krawiecka M, Goldberg D, Vaughan M. A standardised psychiatric assessment scale for rating chronic psychotic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1977;55:299‐308. - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79:231‐8. - PubMed
Leucht 2005b
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale Scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. - PubMed
Leucht 2012
Lieberman 2005
-
- Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(12):1209‐23. - PubMed
Mangalore 2007
-
- Mangalore R, Knapp M. Cost of schizophrenia in England. Journal of Mental Health Policy and Economics 2007;10:23–41. - PubMed
Marshall 1998
-
- Marshall M. Personal communication 1998. Personal communication.
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Adams C, Bradley C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales ‐ a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia?. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;39:337‐49. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D, CONSORT Group (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials). The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285(15):1987‐1. - PubMed
Murray 2012
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability‐adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990‐2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2197‐223. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4] - DOI - PubMed
NICE Guideline:CGS 82 Schizophrenia (update) 2009
-
- Core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in adults in primary and secondary care. NICE Guideline:CGS 82 Schizophrenia (update). - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Priest 1977
-
- Priest RG, Steiner J. Insanity: A study of Major Psychiatric Disorders. Plymouth: Macdonald and Evans, 1977.
Rust 1989
-
- Rust J, Golombok S. Modern Psychometrics. London: Routledge, 1989.
Saikia 1983
-
- Saikia JK, Jørgensen A. Steady‐state serum concentrations after cis(Z)‐flupentixol decanoate in Viscoleo(R). Psychopharmacology 1983;80:371‐3. - PubMed
Sartorius 2002
Schulz 1994
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Grimes DA, Altman DG. Assessing the quality of randomization from reports of controlled trials published in obstetrics and gynaecology journals. JAMA 1994;272:125‐8. - PubMed
Schünemann 2008
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008:359‐83.
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1970;212(Suppl 1):11‐9. - PubMed
Thornicroft 2006
-
- Thornicroft G. Shunned: Discrimination Against People with Mental Illness. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006.
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):3‐92. - PubMed
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

