Chronic D-serine reverses arc expression and partially rescues dendritic abnormalities in a mouse model of NMDA receptor hypofunction
- PMID: 24915645
- PMCID: PMC4122302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2014.05.015
Chronic D-serine reverses arc expression and partially rescues dendritic abnormalities in a mouse model of NMDA receptor hypofunction
Abstract
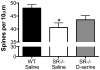
Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) is an immediate early gene that is expressed almost exclusively in glutamatergic neurons. Arc protein is enriched in the postsynaptic density (PSD) and colocalizes with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) complex. Arc transcription is positively modulated by NMDAR activity and is important for dendritic spine plasticity. Genetic ablation of serine racemase (SR-/-), the enzyme that converts L-serine to D-serine, a coagonist at the NMDAR, reduces dendritic spine density in the hippocampus. Here we demonstrate that SR deficient (SR-/-) mice also have reduced Arc protein expression in the hippocampus that can be reversed with chronic D-serine administration in adulthood. Furthermore, D-serine treatment partially rescues the hippocampal spine deficit in SR-/- mice. These results demonstrate the importance of D-serine in regulating the hippocampal expression of Arc in vivo. In addition, our findings underscore the potential utility of using the glycine modulatory site agonist D-serine to treat disorders that exhibit Arc and dendritic spine dysregulation as a consequence of NMDAR hypofunction, such as schizophrenia.
Keywords: Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein; Dendritic spines; Dentate gyrus; Schizophrenia; Serine racemase.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Balu has no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fromer M, Pocklington AJ, Kavanagh DH, Williams HJ, Dwyer S, Gormley P, Georgieva L, Rees E, Palta P, Ruderfer DM, Carrera N, Humphreys I, Johnson JS, Roussos P, Barker DD, Banks E, Milanova V, Grant SG, Hannon E, Rose SA, Chambert K, Mahajan M, Scolnick EM, Moran JL, Kirov G, Palotie A, McCarroll SA, Holmans P, Sklar P, Owen MJ, Purcell SM, O’Donovan MC. De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature 2014 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

