Neuropeptide S receptor 1 (NPSR1) activates cancer-related pathways and is widely expressed in neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 24915894
- PMCID: PMC4116602
- DOI: 10.1007/s00428-014-1602-x
Neuropeptide S receptor 1 (NPSR1) activates cancer-related pathways and is widely expressed in neuroendocrine tumors
Erratum in
- Virchows Arch. 2014 Aug;465(2):251. Dario, G [corrected to Grecco, D]
Abstract
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) arise from disseminated neuroendocrine cells and express general and specific neuroendocrine markers. Neuropeptide S receptor 1 (NPSR1) is expressed in neuroendocrine cells and its ligand neuropeptide S (NPS) affects cell proliferation. Our aim was to study whether NPS/NPSR1 could be used as a biomarker for neuroendocrine neoplasms and to identify the gene pathways affected by NPS/NPSR1. We collected a cohort of NETs comprised of 91 samples from endocrine glands, digestive tract, skin, and lung. Tumor type was validated by immunostaining of chromogranin-A and synaptophysin expression and tumor grade was analyzed by Ki-67 proliferation index. NPS and NPSR1 expression was quantified by immunohistochemistry using polyclonal antibodies against NPS and monoclonal antibodies against the amino-terminus and carboxy-terminus of NPSR1 isoform A (NPSR1-A). The effects of NPS on downstream signaling were studied in a human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line which overexpresses NPSR1-A and is of neuroendocrine origin. NPSR1 and NPS were expressed in most NET tissues, with the exception of adrenal pheochromocytomas in which NPS/NPSR1 immunoreactivity was very low. Transcriptome analysis of NPSR1-A overexpressing cells revealed that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, circadian activity, focal adhesion, transforming growth factor beta, and cytokine-cytokine interactions were the most altered gene pathways after NPS stimulation. Our results show that NETs are a source of NPS and NPSR1, and that NPS affects cancer-related pathways.
Figures


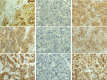

References
-
- Pulkkinen V, Majuri ML, Wang G, Holopainen P, Obase Y, Vendelin J, Wolff H, Rytilä P, Laitinen LA, Haahtela T, Laitinen T, Alenius H, Kere J, Rehn M. Neuropeptide S and G protein-coupled receptor 154 modulate macrophage immune responses. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1667–1679. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl090. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yao Y, Su J, Yang G, Zhang G, Lei Z, Zhang F, Li X, Kou R, Liu Y, Liu J. Effects of neuropeptide S on the proliferation of splenic lymphocytes, phagocytosis, and proinflammatory cytokine production of pulmonary alveolar macrophages in the pig. Peptides. 2011;32:118–124. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.09.021. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

