Rhodium-catalyzed B-H activation of 1,2-azaborines: synthesis and characterization of BN isosteres of stilbenes
- PMID: 24916200
- PMCID: PMC4068778
- DOI: 10.1021/ol501362w
Rhodium-catalyzed B-H activation of 1,2-azaborines: synthesis and characterization of BN isosteres of stilbenes
Abstract
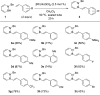
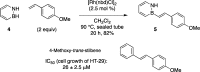
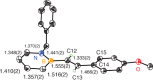
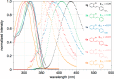
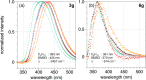
The first example of catalytic B-H activation of azaborines leading to a new family of stilbene derivatives through dehydrogenative borylation is reported. Ten 1,2-azaborine-based BN isosteres of stilbenes have been synthesized using this method, including a BN isostere of a biologically active stilbene. It is demonstrated that BN/CC isosterism in the context of stilbenes can lead to significant changes in the observed photophysical properties such as higher quantum yield and a larger Stokes shift. Direct comparative analysis of BN stilbene 3g and its carbonaceous counterpart 6g is consistent with a stronger charge-transfer character of the excited state exhibited by 3g in which the 1,2-azaborine heterocycle serves as a better electron donor than the corresponding arene.
Figures

References
-
- Roupe K. A.; Remsberg C. M.; Yáñez J. A.; Davies N. M. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 81–101. - PubMed
-
-
For pioneering mechanistic work on the photoisomerization of stilbenes, see:
- Saltiel J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 1036–1037.
- Saltiel J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 6394–6400.
- Saltiel J.; Waller A. S.; Sears D. F. Jr; Garrett C. Z. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 2516–2522.
-
-
- Cheng L. T.; Tam W.; Stevenson S. H.; Meredith G. R.; Rikken G.; Marder S. R. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 10631–10643.
-
- Lo S.-C.; Burn P. L. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1097–1116. - PubMed
- Likhtenshtein G.Stilbenes: Applications in Chemistry, Life Sciences, and Materials science; Wiley: New York, 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

