Gluconate 5-dehydrogenase (Ga5DH) participates in Streptococcus suis cell division
- PMID: 24916441
- PMCID: PMC4180457
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-014-0074-8
Gluconate 5-dehydrogenase (Ga5DH) participates in Streptococcus suis cell division
Abstract
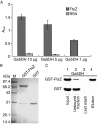
Bacterial cell division is strictly regulated in the formation of equal daughter cells. This process is governed by a series of spatial and temporal regulators, and several new factors of interest to the field have recently been identified. Here, we report the requirement of gluconate 5-dehydrogenase (Ga5DH) in cell division of the zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis. Ga5DH catalyzes the reversible reduction of 5-ketogluconate to D-gluconate and was localized to the site of cell division. The deletion of Ga5DH in S. suis resulted in a plump morphology with aberrant septa joining the progeny. A significant increase was also observed in cell length. These defects were determined to be the consequence of Ga5DH deprivation in S. suis causing FtsZ delocalization. In addition, the interaction of FtsZ with Ga5DH in vitro was confirmed by protein interaction assays. These results indicate that Ga5DH may function to prevent the formation of ectopic Z rings during S. suis cell division.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

