Unusual interaction of RNA polymerase with the bacteriophage Mu middle promoter Pm in the absence of its activator protein Mor
- PMID: 24916637
- PMCID: PMC4287176
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.181
Unusual interaction of RNA polymerase with the bacteriophage Mu middle promoter Pm in the absence of its activator protein Mor
Abstract
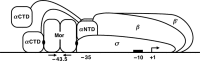
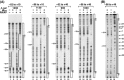
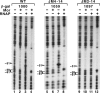
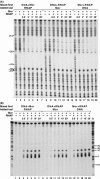
The bacteriophage Mu Mor activator protein is absolutely required for transcription from the Mu middle promoter P(m). However, when RNA polymerase (RNAP) was incubated with P(m) DNA in the absence of Mor, a band at promoter position -51 was hypersensitive to DNase I cleavage, demonstrating an interaction of RNAP with the promoter DNA. The hypersensitivity was similar at four different lengths of P(m) DNA assayed from -62 to +10, -62 to +46, -96 to +10, and -96 to +46. The hypersensitivity occurred equally well at 5 °C, 15 °C, and 30 °C, indicating that it did not require open complex formation, which only occurred at 30 °C. The -51 hypersensitivity at 5 °C and 15 °C was eliminated by the addition of heparin, consistent with the possibility that it arose by formation of unstable closed complexes of RNAP bound to P(m) DNA. Generation of the hypersensitive band required the complete RNAP with its αCTDs, but neither the αCTD nor intact α were sufficient for the interaction and resulting hypersensitivity. There was no correlation between the level of hypersensitivity observed in vitro and the level of Pm activity in vivo, as assayed by the Mor-dependent production of β-galactosidase from a P(m)-lacZ fusion. In an "order of addition" experiment, preincubation of P(m) DNA with Mor followed by addition of RNAP led to the fastest open complex formation, whereas preincubation of P(m) DNA with RNAP gave the slowest. These results support the conclusion that Mor recruits RNAP to P(m) rather than reposition a prebound RNAP, as occurs for C-dependent repositioning of RNAP at the Mu late promoter Pmom .
Keywords: Bacteriophage Mu; Mor activator protein; Mu middle promoter Pm; RNAP-promoter interactions; prokaryotic transcription.
© 2014 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
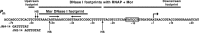


References
-
- Artsimovitch I, Murakami K, Ishihama A. Howe MM. Transcription activation by the bacteriophage Mu Mor protein requires the C-terminal regions of both alpha and sigma70 subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:32343–32348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

