Pnpla3I148M knockin mice accumulate PNPLA3 on lipid droplets and develop hepatic steatosis
- PMID: 24917523
- PMCID: PMC4262735
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.27242
Pnpla3I148M knockin mice accumulate PNPLA3 on lipid droplets and develop hepatic steatosis
Abstract
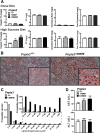
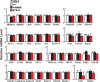
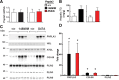
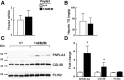
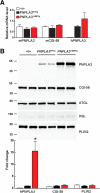
A sequence polymorphism (rs738409, I148M) in patatin-like phospholipid domain containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) is strongly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but the mechanistic basis for this association remains enigmatic. Neither ablation nor overexpression of wild-type PNPLA3 affects liver fat content in mice, whereas hepatic overexpression of the human 148M transgene causes steatosis. To determine whether the 148M allele causes fat accumulation in the liver when expressed at physiological levels, we introduced a methionine codon at position 148 of the mouse Pnpla3 gene. Knockin mice had normal levels of hepatic fat on a chow diet, but when challenged with a high-sucrose diet their liver fat levels increased 2 to 3-fold compared to wild-type littermates without any associated changes in glucose homeostasis. The increased liver fat in the knockin mice was accompanied by a 40-fold increase in PNPLA3 on hepatic lipid droplets, with no increase in hepatic PNPLA3 messenger RNA (mRNA). Similar results were obtained when the catalytic dyad of PNPLA3 was inactivated by substituting the catalytic serine with alanine (S47A).
Conclusion: These data provide the first direct evidence that physiological expression of PNPLA3 148M variant causes NAFLD, and that the accumulation of catalytically inactive PNPLA3 on the surfaces of lipid droplets is associated with the accumulation of TG in the liver.
© 2014 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc., on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



Comment in
-
PNPLA3 I148M variant is associated with metabolic stress-response phenotype in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2015 May;61(5):1769. doi: 10.1002/hep.27390. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25146957 No abstract available.
-
Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 and liver disease: opportunities to unravel mechanisms underlying statistical associations.Hepatology. 2015 Jan;61(1):18-20. doi: 10.1002/hep.27445. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25234690 No abstract available.
-
Potential mechanism underlying the PNPLA3(I) (148) (M) -Hepatic steatosis connection.Hepatology. 2016 Feb;63(2):676-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.27943. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26096616 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Hepatology. 2016 Feb;63(2):677. doi: 10.1002/hep.27945. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26099489 No abstract available.
-
The fat droplet in hepatocellular ballooning and implications for scoring nonalcoholic steatohepatitis therapeutic response.Hepatology. 2016 Mar;63(3):1056-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.28009. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26206460 No abstract available.
References
-
- Singal AK, Guturu P, Hmoud B, Kuo YF, Salameh H, Wiesner RH. Evolving frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation based on etiology of liver disease. Transplantation. 2013;95:755–760. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–690. - PubMed
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Smits MM, Ioannou GN, Boyko EJ, Utzschneider KM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as an independent manifestation of the metabolic syndrome: results of a US national survey in three ethnic groups. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:664–670. - PubMed
-
- McCullough AJ. The clinical features, diagnosis and natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:521–533, viii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
